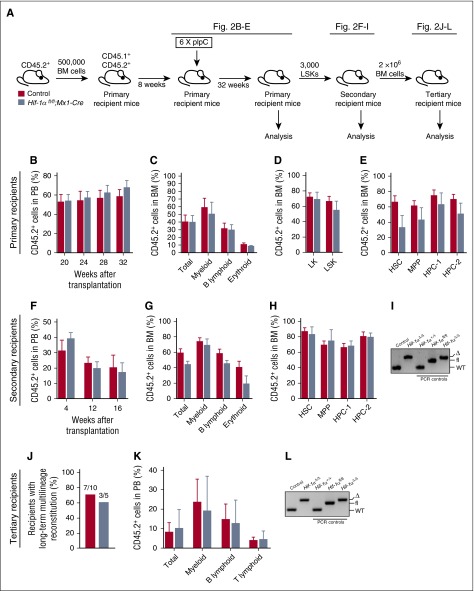
Figure 2.
Prolonged Hif-1α deficiency does not affect the steady-state maintenance of HSCs and their regenerative capacity. (A) Experimental design. Primary recipient mice were transplanted with 500 000 donor-derived unfractionated BM cells from untreated Hif-1αfl/fl;Mx1-Cre and control mice (together with 500 000 CD45.1+ competitor BM cells). Eight weeks posttransplantation, the mice received 6 doses of pIpC. The mice were analyzed 32 weeks after the last dose of pIpC. CD45.2+ LSK cells from the primary recipients were transplanted into secondary recipients. A total of 2 × 106 total BM cells from secondary recipients were transplanted into tertiary recipients together with 200 000 CD45.1+ unfractionated BM cells. (B) CD45.2+ donor-derived PB chimerism 20, 24, 28, and 32 weeks after the last dose of pIpC. Mean ± SEM (n = 5-7 per group). (C) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in total BM, myeloid, B lymphoid, and erythroid cell compartments of primary recipients 32 weeks after pIpC treatment. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5-7 per group). (D-E) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in the indicated hematopoietic compartments of the primary recipients. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5-7 per group). (F) LSK cells of indicated genotypes were pooled from primary recipients 32 weeks after pIpC treatment and transplanted into secondary recipients. The graph shows CD45.2+ donor-derived PB chimerism in secondary recipient mice 4, 12 and 16 weeks after transplantation. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4-7 per group). (G) CD45.2+ donor-derived chimerism within the total BM cell fraction, and myeloid, B lymphoid, and erythroid cell compartments of secondary recipient mice 16 weeks after transplantation. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4-7 per group). (H) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in the indicated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell compartments of the secondary recipients. Mean ± SEM (n = 4-7 per group). (I) PCR amplification of genomic DNA from donor-derived CD45.2+ cell fraction of the PB of secondary recipient mice 12 weeks posttransplantation. For PCR controls, we used genomic DNA from c-Kit+ cells from BM of Hif-1α+/+, Hif-1αfl/fl, and Hif-1αfl/fl;Vav-iCre mice. (J) Results of tertiary transplantation assays. The graph depicts the percentage of tertiary recipients with long-term multilineage reconstitution (>0.5% of donor-derived myeloid and lymphoid cells in PB) 16 weeks after tertiary transplantation of 2 × 106 total BM cells obtained from the secondary recipients (n = 5-10 per genotype). (K) Percentage of CD45.2+ cells in white blood cell (total) compartment, and myeloid, B lymphoid, and T lymphoid cell compartments of PB in tertiary recipients 16 weeks after transplantation. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5-10 per group). (L) Hif-1α gene deletion was confirmed by PCR on genomic DNA from donor-derived CD45.2+ cell fraction of the BM of tertiary recipients 16 weeks posttransplantation. For PCR controls, we used genomic DNA from c-Kit+ cells from BM of Hif-1α+/+, Hif-1αfl/fl, and Hif-1αfl/fl;Vav-iCre mice. At least 2 independent experiments were performed for all analyses.