Figure 1.
Cells Showing PCNA Accumulation on Chromatin Caused by Truncation of ELG1 Exhibit Increased Sensitivity to MMS
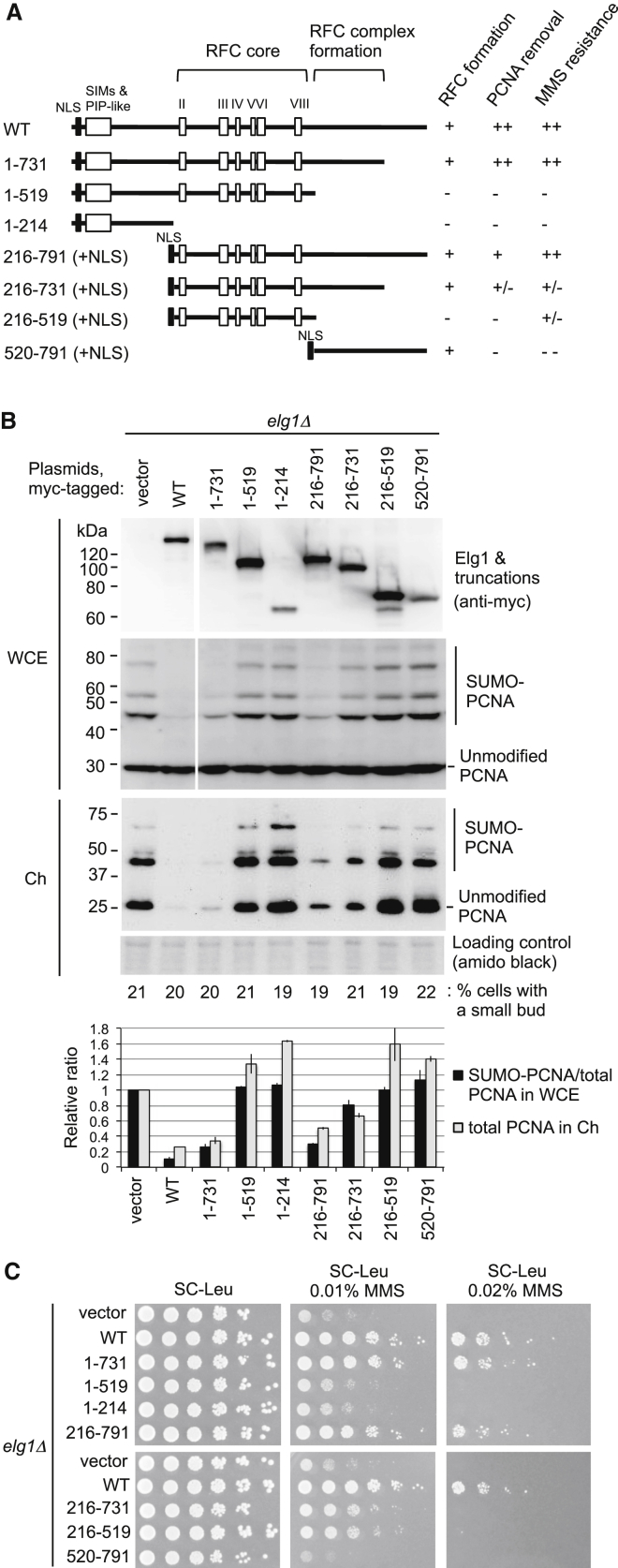
(A) Schematic structure of Elg1 and truncated mutants. Interaction of truncated Elg1 with Rfc4 (RFC formation) was examined previously (Davidson and Brown, 2008). NLS, nuclear localization signal; SIMs, SUMO interacting motifs; PIP-like, PCNA interacting peptide-like motif.
(B) Accumulation of SUMO-PCNA in whole-cell extracts and PCNA on chromatin in cells expressing truncated Elg1 fragments. Whole-cell extracts (WCE) and chromatin-enriched fractions (Ch) were prepared from elg1Δ cells, carrying the empty plasmid or plasmids containing truncated alleles of ELG1, in log phase. Truncated Elg1 and PCNA were detected by western blotting. Percentage of cells with small buds, indicative of cells in S phase, is shown below blots. Quantification of average of two experiments was shown. Error bars, SDs.
(C) Sensitivity to MMS of elg1Δ cells carrying the empty plasmid or plasmids containing truncated alleles of ELG1. 5-fold serial dilutions of cells were spotted on synthetic medium lacking leucine with 2% glucose, plus or minus MMS, and incubated for 3–4 days at 30°C.
See also Figure S4.