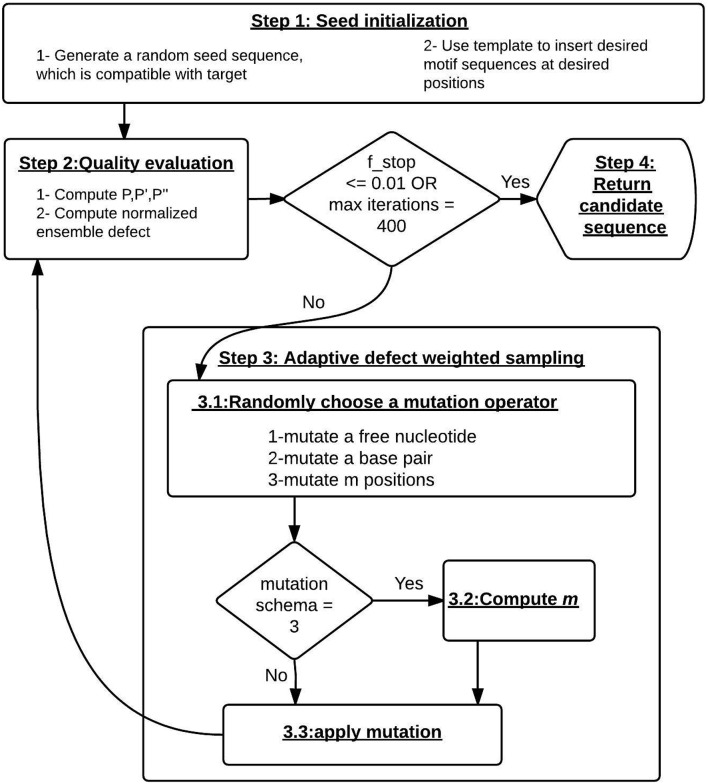
Figure 1.
The design pipeline of Enzymer. Step 1: we generate a random seed sequence, which is compatible with the target. Step 2: we evaluate the quality of the sequence. If the of the stop condition is met, we return the sequence. Step 3: the adaptive defected weighted sampling process starts here. In 3.1 the mutation operator is uniformly randomly selected. If the m-mutation schema is chosen. In step 3.2 we compute the value of m. In 3.3 we sample from low ensemble defect mutational landscape of the current sequence by applying the mutation operator. Step 4: when the stop condition is reached, we return the designed sequence.