Figure 1.
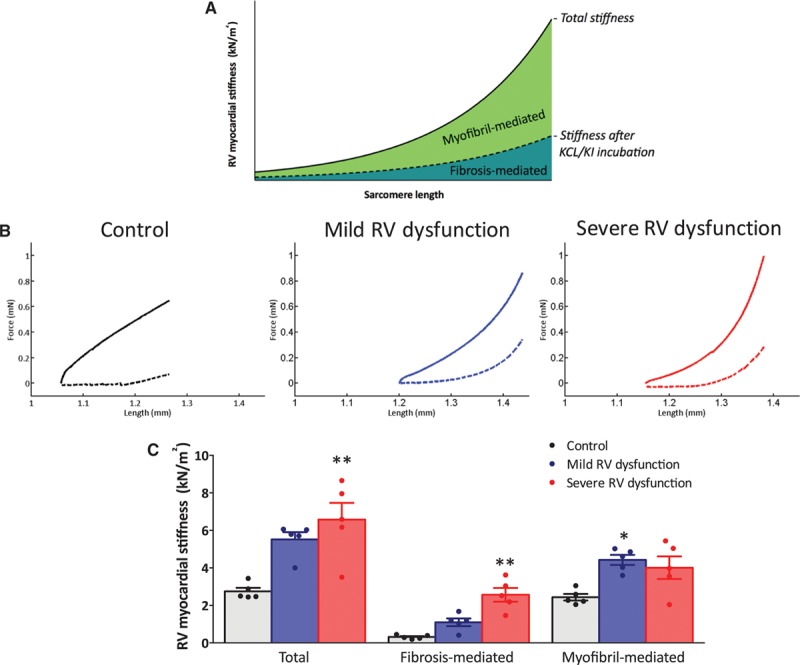
Right ventricular (RV) myocardial stiffness in skinned trabecular strips. A, Schematic representation of skinned trabecular strip measurements. B, Representative examples of RV myocardial stiffness measurements in skinned trabecular strips of control, mild RV dysfunction, and severe RV dysfunction before (solid line) and after incubation with KCl/KI. C, Total RV myocardial stiffness was significantly increased in both mild RV dysfunction (blue bars) and severe RV dysfunction (red bars) in comparison to controls (white bars). In severe RV dysfunction, increased RV myocardial stiffness could be explained by both increased fibrosis- and myofibril-mediated stiffness, whereas in mild RV dysfunction only myofibril-mediated stiffness was increased in comparison to control. Data are presented as mean±SEM. Controls: n=5, mild RV dysfunction: n=5, and severe RV dysfunction: n=5. **P<0.01 vs control.
