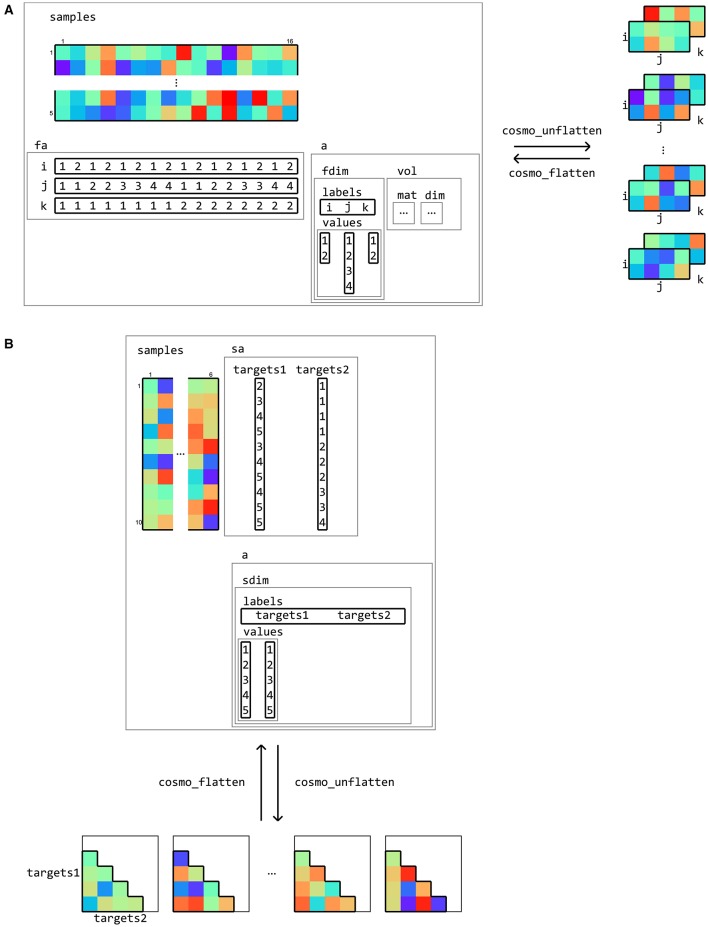
Figure 7.
Flattening and unflattening datasets. A (tiny) fMRI dataset (A) with three spatial dimensions (left) is unflattened along the feature dimension using cosmo_unflatten. Each sample (row) in samples results in a three-dimensional array (right). (B) a dataset containing representational dissimilarities for five conditions is unflattened along the sample dimension. Each column in samples result in a dissimilarity matrix. The result from unflattening a dataset can be reversed in both (A,B) using cosmo_flatten. Note that dataset input/output functions for volumetric, surface-based, and M/EEG data (Figure 10) use the flattening and unflattening operations internally.