Fig. 1.
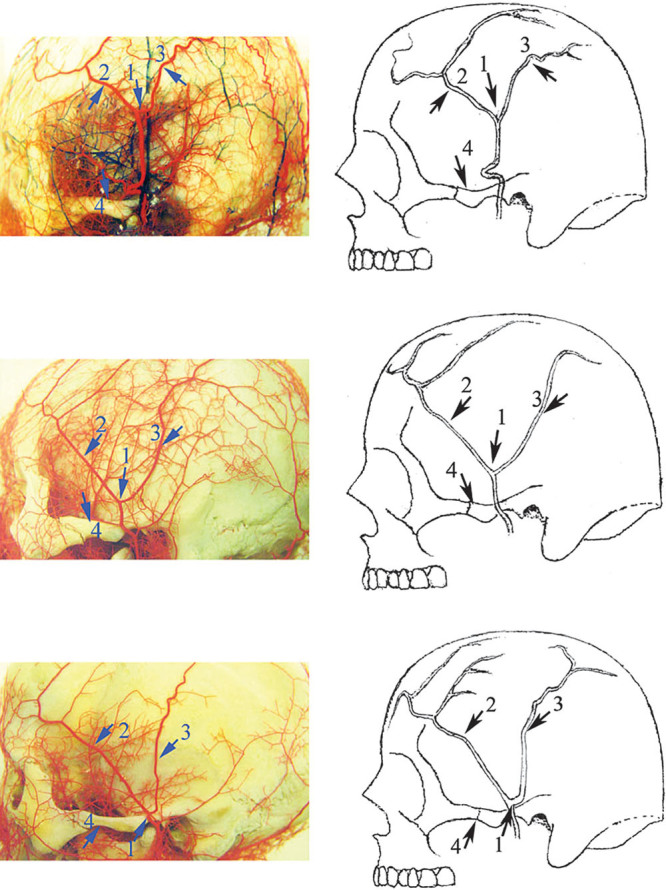
Illustrations of common branch patterns of the frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery. At the bifurcation point, 1, the superficial temporal artery divides into the anterior frontal branch, 2, and the posterior parietal branch, 3. The frontal branch can be classified as high-location type (64%) and low-location type (36%) based on its relationship to the horizontal line of the superior orbital rim. Eighty-four percent of the frontal branch originates at the level superior to the zygomatic arch, 4. The course of the main branch of the frontal branch can be classified as either linear or circuitous. As the bifurcation point rises, the inclination increases and the obliquely running frontal branch becomes horizontal. Reprinted with permission from Lei T, Xu DC, Gao JH, et al. Using the frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery as a landmark for locating the course of the temporal branch of the facial nerve during rhytidectomy: an anatomical study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:623–629; discussion 630.
