Figure 1. Internuclear transcriptional organization.
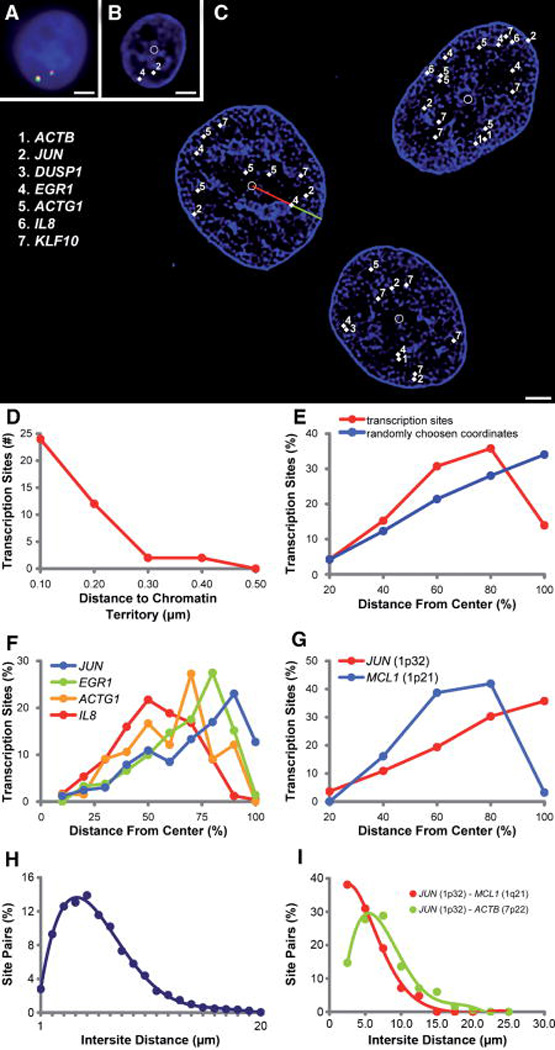
A: Multiplexed FISH detects transcription, the multi-colored foci, in a DAPI-stained nucleus (blue). (Bar = 1 µm). B: The transcription sites, labeled with binary combinations of four dyes, are identified and annotated by software (white diamonds, numbers corresponding to key, inset in C). The deconvolved DAPI data reveal boundaries of heterochromatin domains. Software labels the nuclear geometric centroid (white circle). (Bar = 1 µm). C: Three human adenocarcinoma (DLD-1) G2 nuclei with labeled transcription sites (key inset) and geometric centroids (white circles) and heterochromatin domains (blue). Software measures the relative radial position of each transcription site by normalizing the distance from the nuclear centroid to the transcription site (red line) by the distance of a line from the nuclear centroid to the edge of the nucleus intersecting the transcription site (green and red line combined, see Methods). (Bar = 3 µm). D: Histogram of distances between 40 transcription sites and the closest heterochromatin domain. Ninety percent of sites are within 200 nm of heterochromatin domains. E: The radial distribution of 1,285 transcription sites differs significantly (P = 0.0048) from the distribution of twice the number of points randomly generated within the same nuclear bounds. F: Four significantly distinct radial distributions were associated with the actively transcribing genes ACTG1, IL8, EGR1, and JUN (Mann-Whitney P = 0.0029, 0.0061, 0.0043, respectively). G: Genes from the same chromosome can be resolved and show directionality of the chromatin territories. MCL1, from the q-arm of chromosome 1 is centrally located relative to the locus ofJUN, which resides on the p-arm (P = 0.0044). H: The intranuclear distance between each transcription site was measured and is normally distributed. I: The distances between transcription sites expressed from the same chromosome are shorter than the distances between unlinked sites.
