Figure 1.
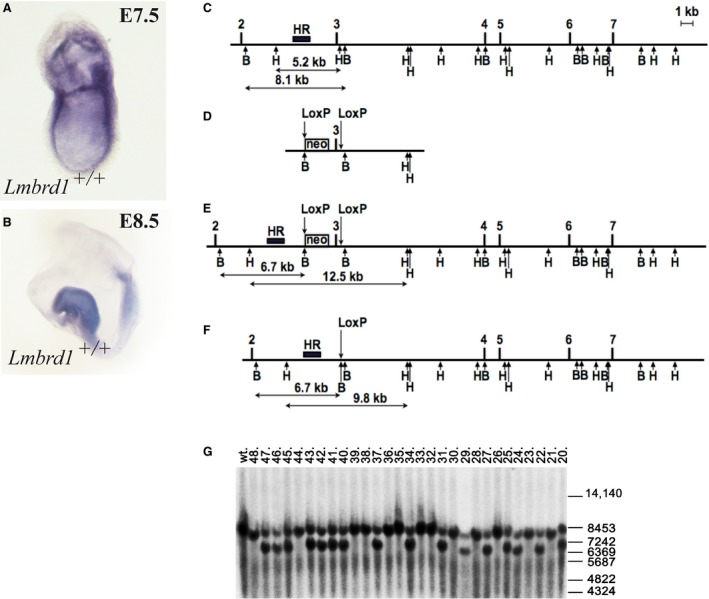
Expression of Lmbrd1 and generation of Lmbrd1 −/−‐mice. (A and B) Lateral view of C57BL/6J wild‐type embryos stained by whole mount in situ hybridization. Lmbrd1 is ubiquitously expressed at the embryonic stage E7.5 and more restricted to neuronal folds at E8.5. (C–F) Targeting of the exon 3 of mouse Lmbrd1 gene. The intronic and intergenic regions are shown as lines, exons are shown as filled boxes. Exons numeration is shown above. The empty box corresponds to the neomycin resistance cassette (neo) flanked by FRT sites (data not shown). The arrows above correspond to the LoxP sequences, and arrows below correspond to restriction endonuclease sites BamHI (B) and HindIII (H). The black box corresponds to the Southern probe sequences (HR). The expected sizes of restriction DNA fragments are labelled below. (C) Wild‐type locus. (D) Targeting vector structure (without negative selection marker and plasmid backbone). (E) Genomic locus after homologous recombination. (F) The neomycin cassette (neo) and the Lmbrd1 exon 3 are removed through breeding with CRE recombinase expressing mice (PGK‐Cre). (G) Southern blot analysis of DNA isolated from Lmbrd1 targeted mice and their wild‐type siblings. Mice numeration is shown on top and positions of the size marker (in bp) are shown on the right. Wild‐type corresponds to DNA sample from wild‐type control mouse. Germline transmission of the targeted Lmbrd1 allele from chimeric mice to offspring. Enzymatic digestion using BamHI and hybridization with the HR probe (wild‐type allele 8.1 kb, targeted allele 6.7 kb) was used to detect the predicted homologous recombination (C and E) in the Lmbrd1 gene locus. Mice 20, 22, 24, 25, 27, 29, 31, 34, 37, 40–43, 45–47 are heterozygous for the targeted Lmbrd1 gene.
