Figure 4.
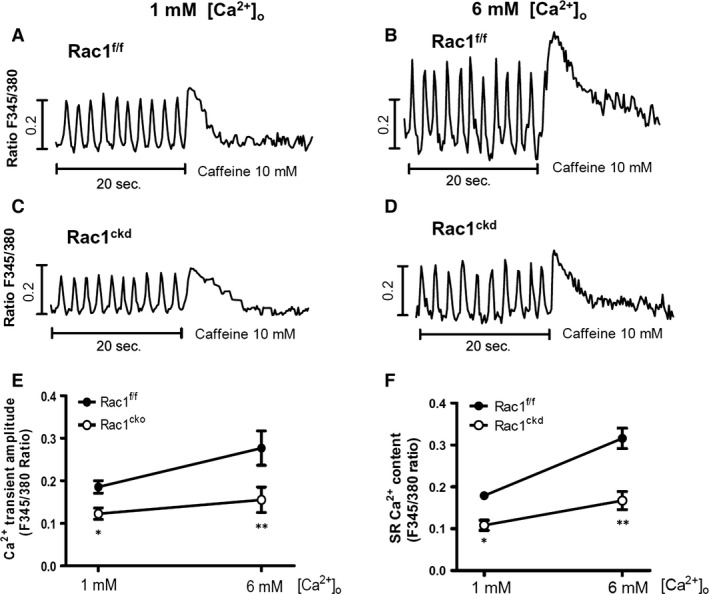
Rac1 inhibition reduces cardiomyocyte Ca2+ transients and sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ load. (A–D) Representative Fura‐2 ratios in Rac1f/f and Rac1ckd myocytes, which were perfused at 1 and 6 mM extracellular Ca2+ concentrations and paced at 0.5 Hz for 20 sec. followed by treatment with caffeine. (E) Ca2+ transient amplitude in Rac1f/f and Rac1ckd myocytes during pacing. (F) SR Ca2+ load assessed by caffeine (10 mM) in Rac1f/f and Rac1ckd myocytes. Data are mean ± SEM of 10–16 myocytes from 3 mice per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus corresponding Rac1f/f.
