FIGURE 5.
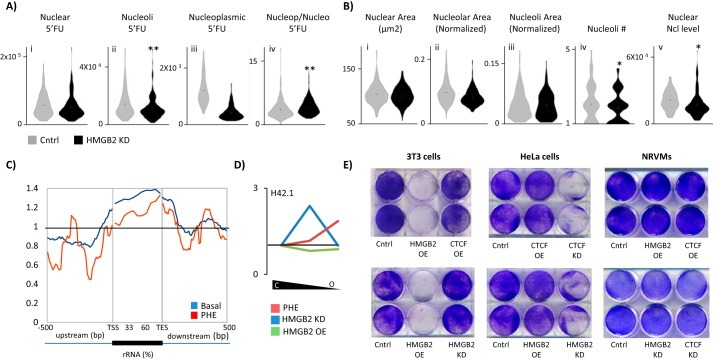
Hmgb2 and Ctcf influence nucleolar rRNA transcription. A, control or hmgb2 knockdown NRVMs were treated with 5′FU to label newly transcribed RNA. hmgb2knockdown decreased nucleolar transcription (nucleoli determined by costaining for nucleolin) while increasing the ratio of nucleoplasmic to nucleolar transcription (n = 186 control, 181 knockdown; ** indicates p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney); one representative experiment of three). B, effect of Hmgb2 on nucleolar transcription could not be explained by changes to nucleolar morphology. (Nucleolar area was determined by nucleolin costaining. Nucleoli area represents area of individual nucleoli, and nucleolar area represents total area of all nucleoli in a nucleus.) However, we found a decrease in the abundance of nucleolin levels (* indicates p < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney); one representative experiment of three). C, Hmgb2 ChIP-seq reads were aligned across ribosomal RNA genes showing Hmgb2 is enriched at these loci in the basal state and 48 h after phenylephrine treatment. D, partial chromatin digestion by micrococcal nuclease was used to isolate euchromatic and heterochromatic DNA in NRVMs followed by qPCR to determine the relative distribution of H42.1, a region of rDNA (see Fig. 7A for schematic). The ratio of intermediately packed chromatin to heterochromatin (center of plot) or euchromatin to heterochromatin (right end of plot) was plotted as a change in the ratio after hmgb2 knockdown or overexpression as compared with basal cells. In the control setting, the majority of H42.1 sequences was in the most heterochromatic fraction. hmgb2 overexpression had little effect on the ratios of heterochromatic and euchromatic rDNA, whereas hmgb2 knockdown increased the ratio of intermediately packed to tightly packed DNA. 48 h after phenylephrine, rDNA was shifted to a more euchromatic environment (average of three separate experiments). E, cell viability was assayed by labeling with crystal violet, which stains living cells. Although the effect of overexpression of hmgb2 was minimal in NRVMs, in dividing 3T3 cells there was a dramatic cell killing effect. In contrast, ctcf or hmgb2 knockdown induced cell death in HeLa cells (representative example of three separate experiments).