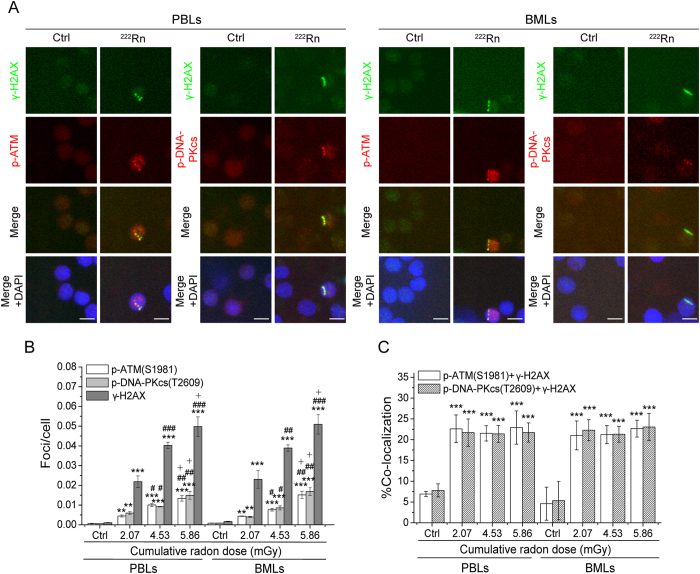
Figure 2. Formation of p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci and their co-localization with γ-H2AX foci in rat PBLs and BMLs induced by radon exposure in vitro.
(A) Representative image showing p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci and their co-localization with γ-H2AX foci in PBLs and BMLs induced by radon exposure in vitro. (B) The dose-response for p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci in PBLs and BMLs induced by in vitro radon exposure. (C) The co-localization ratios of p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci with γ-H2AX foci in PBLs and BMLs induced by in vitro radon exposure. Three thousand to eight thousand lymphocytes from each sample were used for p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs foci quantitation. The data are presented as averages ± standard deviations of four-six rats. Green, γ-H2AX; red, p-ATM and p-DNA-PKcs; blue, DNA stained with DAPI. 1000 × magnification; scale bar, 5 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the background value of control group for the same protein in the same type of cells, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared with the same protein in the same type of cells at the dose of 2.07 mGy, and +P < 0.05 compared with the same protein in the same type of cells at the dose of 4.53 mGy.