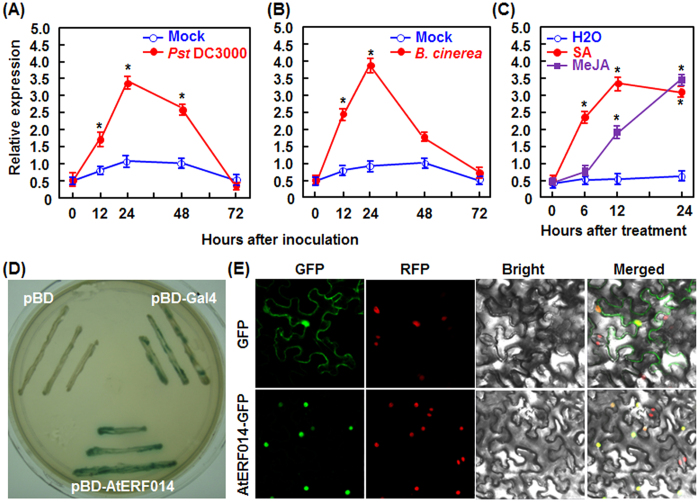
Figure 1. Pathogen-induced expression of AtERF014 and biochemical characteristics of AtERF014.
(A–C) Expression patterns of AtERF014 induced by P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (A) and B. cinerea (B) or by defense signaling hormones (C). Four-week-old plants were inoculated with Pst DC3000, B. cinerea spore suspension, or similar volume of buffer as mock controls (A,B). The Arabidopsis plants were treated by foliar spraying with solutions of 1 mM SA or 100 μM MeJA (C). The transcript level of AtERF014 was analyzed and relative expression is shown as folds of the transcript level of the internal AtActin gene. Data presented are the means ± SD from three independent experiments and * indicates significant difference at p < 0.05 level between the inoculated/treated plants and mock control plants. (D) AtERF014 is a transcription activator. Yeasts harboring pBD-AtERF014, pBD empty vector (a negative control) and pBD-GAL4 (a positive control) were grown on SD/Trp− medium and β-galactosidase activity was examined by addition of X-α-gal. (E) AtERF014 is localized in nucleus. Leaves of Nicotinana benthamiana plants were collected at 24 hr after infiltration of agrobacteria and photos were taken in dark field for GFP and RFP, bright field for cell morphology and in combination (merged), respectively.