Fig. 2.
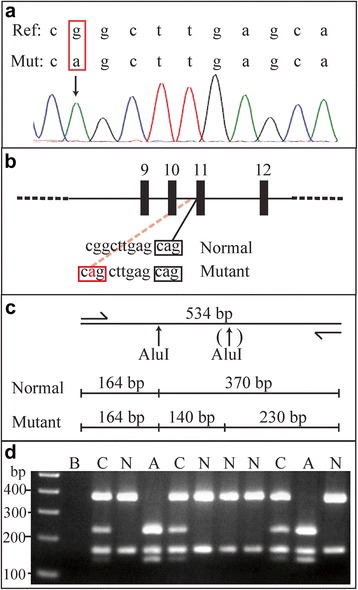
Analyzing the c.1624−11G >A mutation of ZAP70. Panel a - Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA from an affected individual depicting a homozygous intronic g >a mutation. Panel b – A schematic representation of a portion of the ZAP70 gene indicating how the mutation generates a new acceptor sequence in affected individuals. Panel c – A restriction map of the PCR amplified product depicting the position of a second AluI cutting site (↑) in mutated alleles. Panel d - 534 bp PCR products were digested with AluI and the resulting fragments separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1 is a 100 bp DNA standard and Lane 2 is a water blank (B). Lanes 3 through 12 depict fragments generated from individuals of normal (N) genotype (370 bp and 164 bp), affected (A) genotype (230 bp, 164 bp and 140 bp) or carrier (C) genotype (370 bp, 230 bp, 164 bp and 140 bp)
