Figure 4.
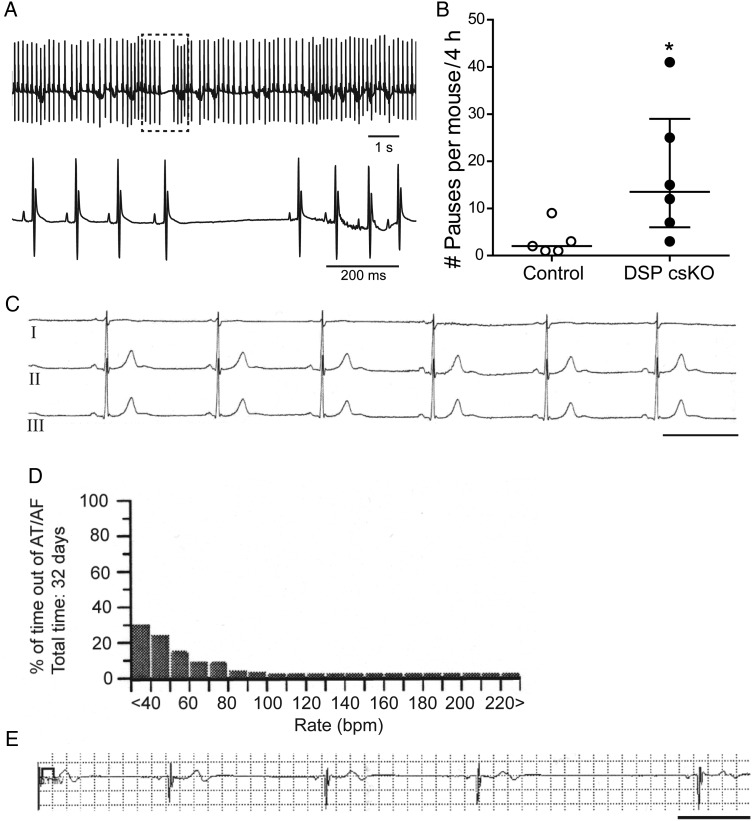
Dysregulation of DSP (loss or mutation) leads to increased sinus pauses in mice and man in vivo. (A) Upper panel: Representative ECG telemetry trace from a DSP csKO mouse. Lower panel: Expanded view of sinus pause in hatched box. (B) Quantification of sinus pauses in a period of 4 h from DSP csKO and littermate control mice. Number of pauses observed from each individual mouse is graphed in circles. Open circles and open bar: Control mice; Closed circles and black bar: DSP csKO mice (n = 5 for control, n = 6 for DSP csKO). *P < 0.05. (C) Lead I–III ECG showing sinus bradycardia (38 bpm) in the 19-year-old patient carrier of the DSP mutation c273 + 5 G > A. Scale bar: 1 s. (D) Ventricular rate histogram from 32 days loop recorder monitoring showing sinus bradycardia with heart rate values <60 bpm for 70% of time. (E) ECG strip recorded by the implantable loop recorder (Medtronic Linq) showing a diurnal sinus pause of 3 s. Scale bar: 1 s.