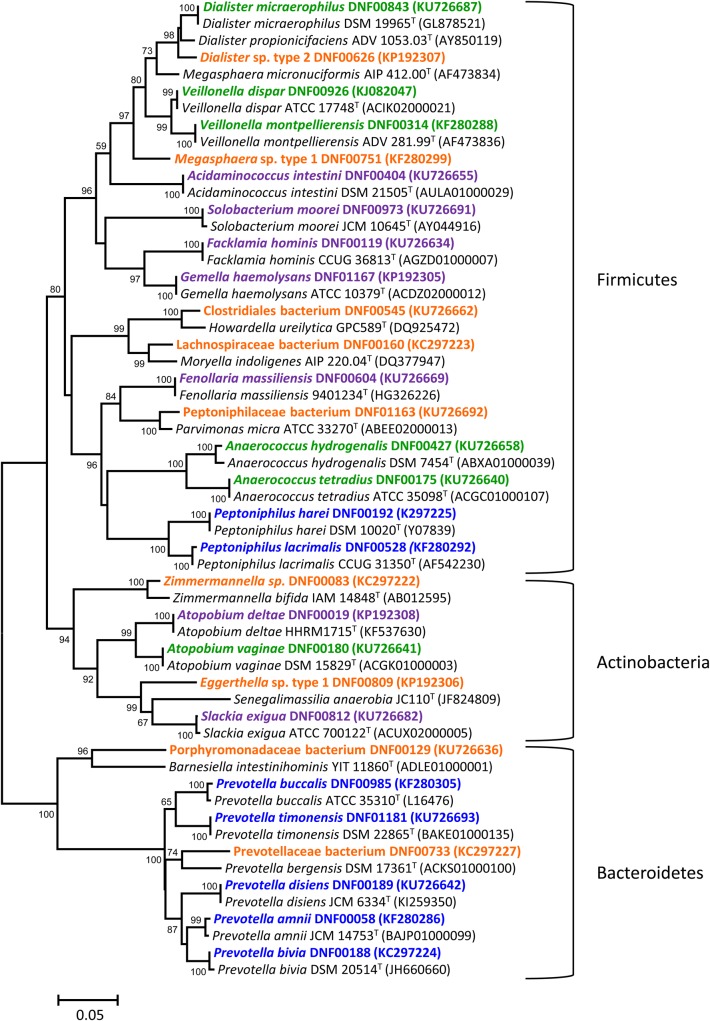
Figure 1.
Diversity of bacterial isolates obtained with classical cultivation methods. Minimum evolution phylogenetic dendrogram shows relationships of representative 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequences of vaginal bacterial isolates among closely related validly described species. Numbers at branch points depict bootstrap support based on analysis of 1000 replicates. GenBank accession numbers for the 16S rRNA sequences are provided in parentheses. Strains are color coded based on categories developed in this study. Orange indicates bacteria with <98% sequence identity to validly published species; blue, closely related species within a genus; purple: bacteria previously isolated from other human body sites but not the vagina; and green, known bacteria previously isolated from the vagina. Bar represents 5% sequence divergence.