Figure 2. TDCS-Linked Far Transfer Benefits.
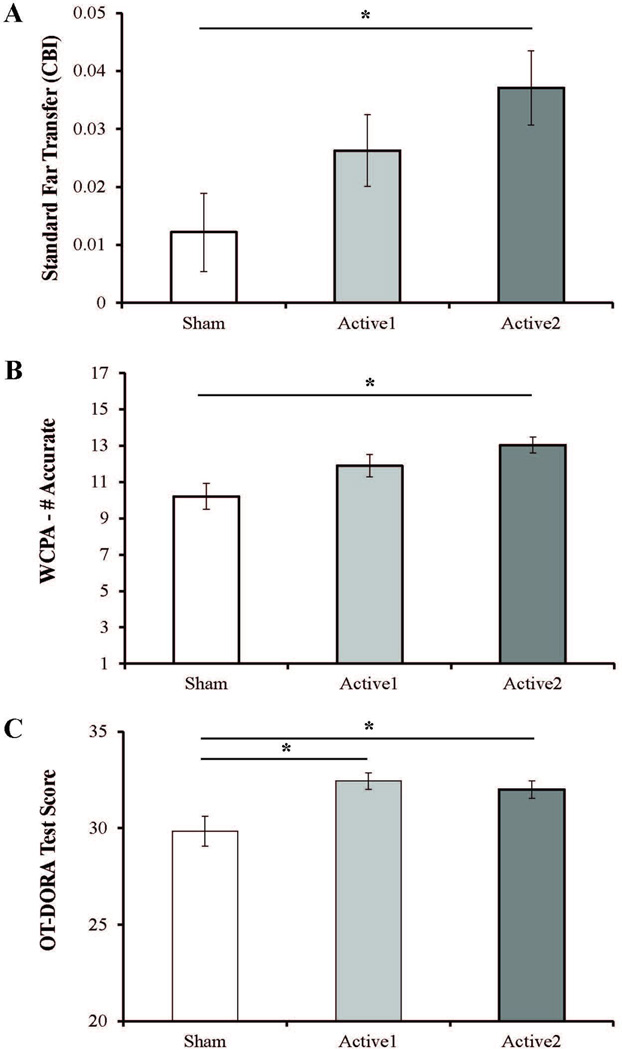
Standard Far Transfer Tasks (A) The CBI (composite benefit index) represents a collective change in performance averaged across 3 standard far transfer tasks with re-test option (Go/No-Go, Functional Math, WAIS Coding). Significant group differences were observed. Active2 had a significantly higher CBI than Sham. No significant differences were observed between Active2 and Active1 or between Active1 and Sham. Ecologically Valid Far Transfer Tasks. (B–C) (B) Significant group differences were observed on the WCPA (max score = 17). Active2 had significantly higher accuracy than Sham. No significant differences were observed between Active2 and Active1 or between Active1 and Sham. (C). Significant group differences were observed on the OT-DORA (max score = 37). Both Active1 and Active2 significantly out-performed Sham. No significant differences were observed between Active1 and Active2. (A–C) Positive values indicate improved performance Error bars represent standard error of the mean; * indicates p<0.05
