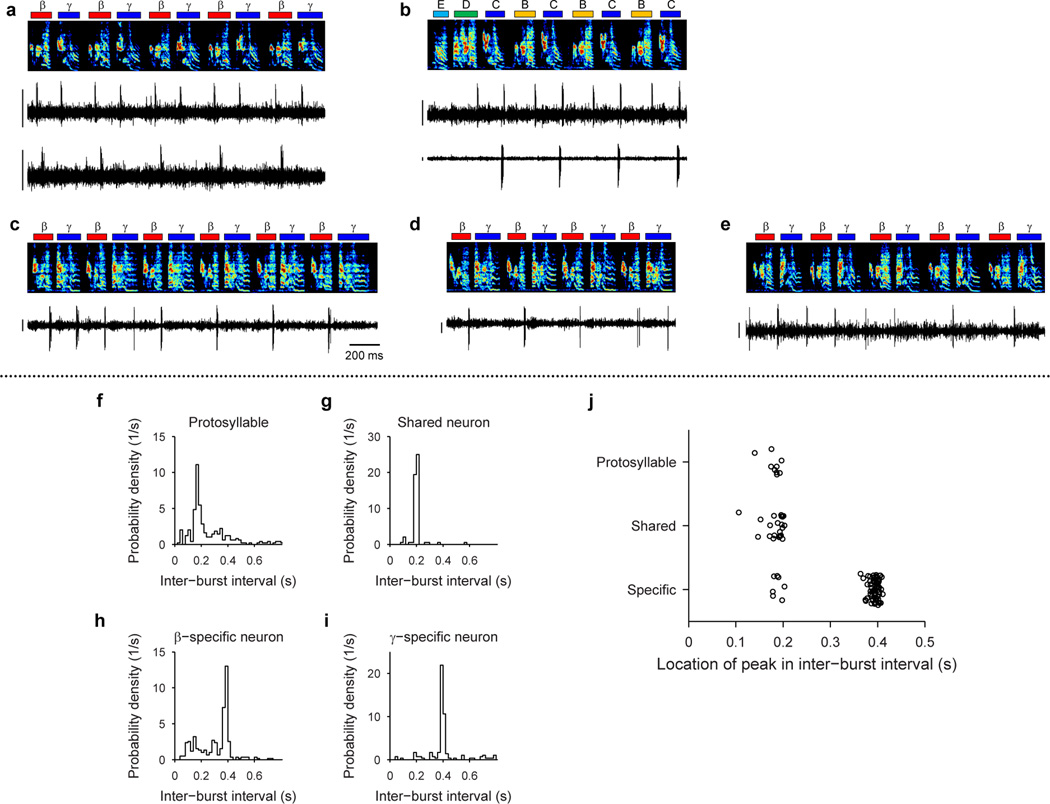
Extended Data Figure 3. Increase in the period of HVC rhythmicity during alternating syllable differentiation.
All data are from Bird 1. a, Paired recording of a shared neuron (top; HVCRA) and a β-specific neuron (bottom; HVCX; 69 dph). b, Paired recording of a shared neuron (top; HVCX) and a C-specific neuron (bottom; HVCX; 110 dph). c, Neuron switching between shared and specific spiking (HVCX; 63 dph). d, Same neuron as in c, switching from specific to shared firing. e, A different neuron switching from shared to specific (HVCp; 68 dph). Scale bars: (a–e) 0.5 mV, 200 ms.
f–i, Inter-burst interval (IBI) distributions for shared and specific neurons. f, for the neuron in Fig. 3c recorded during protosyllable stage. g, for the shared neuron shown in the top panel of Fig. 3f. h, for the β-specific neuron shown in Fig. 3d. i, for a γ-specific neuron (not shown). j, Population summary of the ‘most-probable IBI’ for the neurons recorded during the protosyllable stage (n=9), and during the emergence of syllables β and γ (62–72 dph; shared neurons, n=22; specific neurons, n=83). Note that shared neurons had the same ‘most-probable IBI’ as neurons recorded during the protosyllable stage. Neurons exhibiting an increased burst period by skipping cycles of an underlying rhythm were also observed in Birds 3, 4, and 6 (see Extended Data Fig. 8f–h, 9f, h).