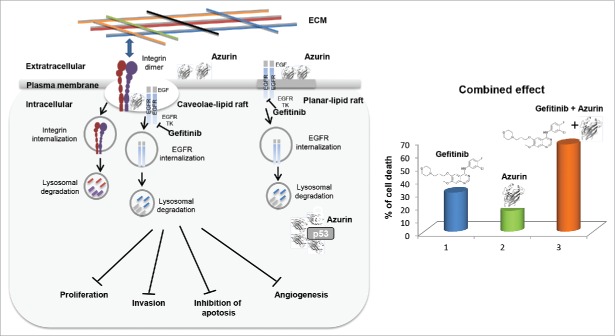
Figure 1.
[Left] Gefitinib binds to the intracellular enzyme (tyrosine kinase) of the EGFR ultimately inducing anti-proliferative effects. Azurin binds to cancer cells through binding to lipid raft components and cell-surface receptors. Upon entry, azurin interferes in cancer cell growth by multiple mechanisms including complex formation with p53. [Right] A dual therapy has demonstrated that azurin enhances the sensitivity of the anticancer drug Gefitinib.