Figure 4. Cx50-CT Directly Interacts with Skp2-NT, whereas the Mutation on V362E Weakens the Interaction.
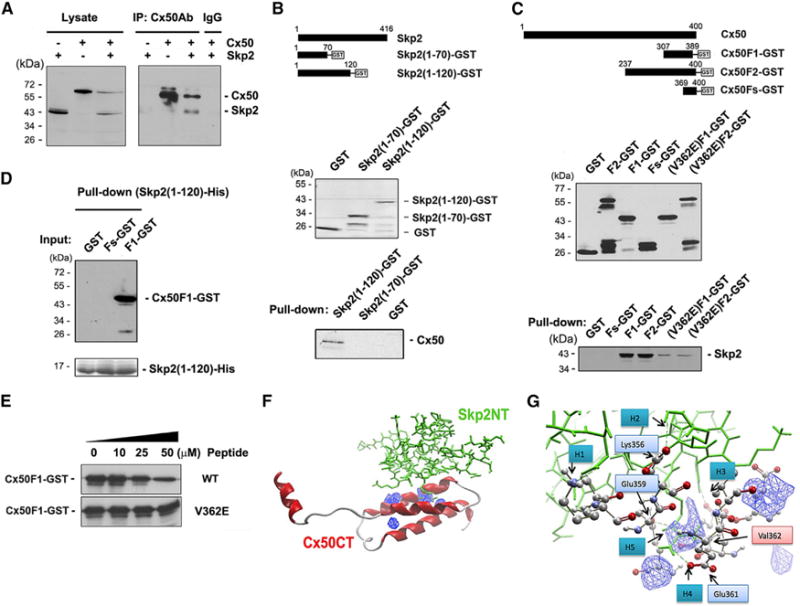
(A) Cx50 associates with Skp2.
(B–D) Cx50-CT directly interacts with Skp2-NT and Cx50(V362E) mutant weakens the interaction. Two GST fusion proteins was generated, Skp2(1-70)-GST and Skp2(1-120)-GST (B, upper). Pull-down assay was conducted with FLAG-tagged Cx50 and Skp2(1-70)-GST or Skp2(1-120)-GST fusion protein (B, lower). Three GST fusion proteins of Cx50-CTs were used for protein pull-down assay (C, upper) with FLAG-tagged Skp2 (C, lower). 9xHis-Skp2-NT was incubated with GST, Fs-GST, or F1-GST-beads (D).
(E) Peptide competition assay by pre-incubating His-Skp2-NT-beads with WT or V362E mutant Cx50-CT, prior to incubation with Cx50-F1-GST.
(F) The hypothetical 3D structure model showing the interaction between Cx50-CT and Skp2-NT. The possible interacting cavities on Cx50-CT were labeled in blue.
(G) Amplified interaction interface between Cx50-CT and Skp2-NT. Amino acids residues on Cx50 involved in this interaction were labeled in light blue boxes and Val-362 in a pink box.
See also Figure S3.
