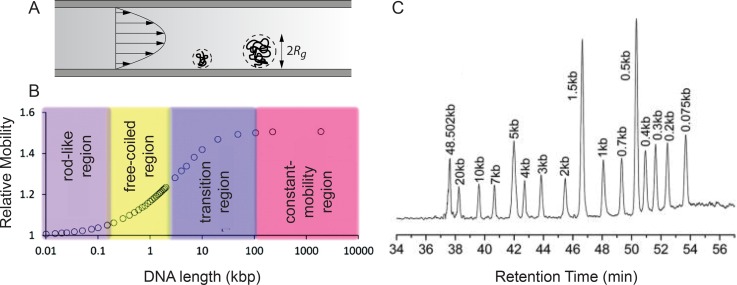
FIG. 11.
(a) Schematic illustration of the mechanism by which larger DNA coils move faster through the capillary when driven by pressure. (b) General relationship between DNA relative mobility and its molecular length within a capillary with radius of 750 nm. (c) Chromatogram corresponding to separation of a mixture of DNA with different molecular lengths. The separation capillary had a radius of 750 nm and a total length of 50 cm. Adapted with permission from Wang et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 7400 (2012). Copyright 2012 American Chemical Society.141