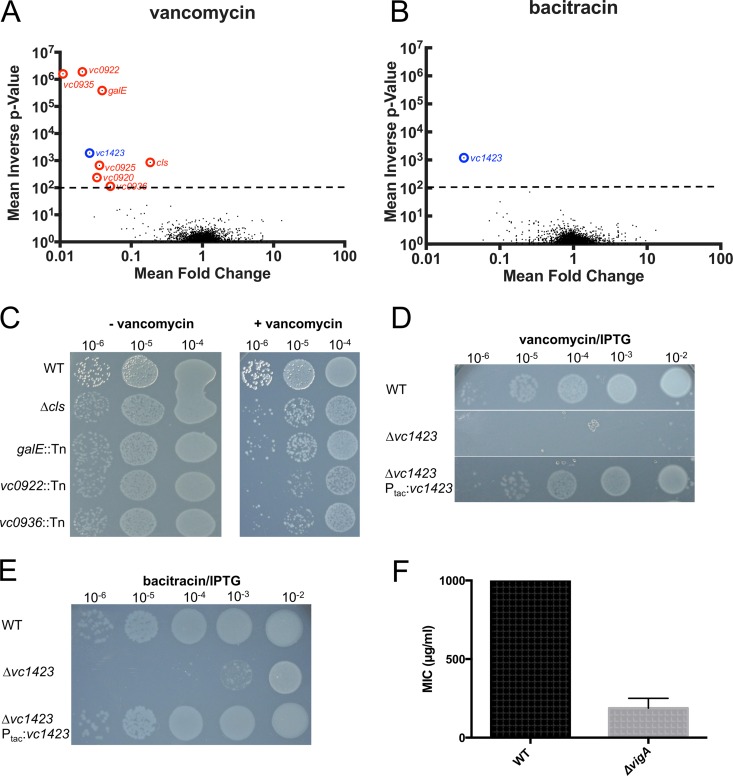
FIG 1.
Identification of genes conferring enhanced susceptibility to vancomycin and bacitracin using transposon insertion sequencing. (A and B) Volcano plots depicting the ratio of read counts mapped to individual genes in transposon libraries plated onto vancomycin (200 μg/ml) (A) or bacitracin (200 μg/ml) (B) compared to control libraries plated onto LB agar without antibiotics (mean fold change, x axis) versus mean P values (y axis) (see Materials and Methods for details). Genes shown in red and blue are considered significantly underrepresented. (C) Validation of plating defects on vancomycin of selected mutants identified in the transposon screen. Mutants were plated onto either LB agar containing vancomycin (200 μg/ml) or LB agar alone (− vancomycin). (D and E) Sensitivity of a V. cholerae vigA mutant (Δvc1423) to vancomycin and bacitracin. Strains (including the Δvc1423 strain ectopically expressing vc1423 under the control of an IPTG-inducible promoter) were spot plated onto agar containing either vancomycin (200 μg/ml) (D) or bacitracin (200 μg/ml) (E) and IPTG (100 μM). (F) Vancomycin MICs of V. cholerae WT and Δvc1423 strains.