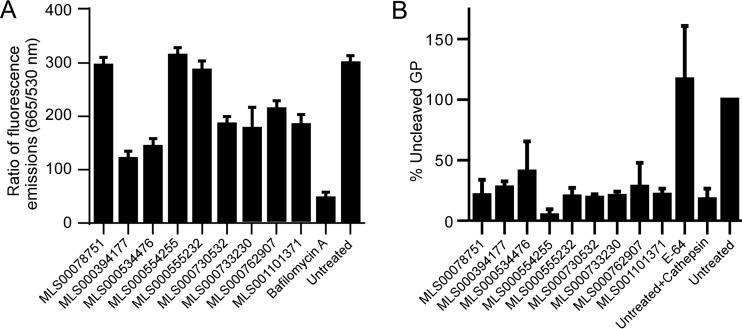
FIG 5.
Effect of compound treatment on interaction with endosomal acidification and cathepsin protease activity. (A) HeLa cells were pretreated with the indicated compounds at 50 μM for 1 h and then incubated for 1 h with acridine orange, a pH-sensitive fluorescent dye that accumulates in endosomes and which has a pH-sensitive fluorescent emission peak measured at 665 nm and a pH-independent emission peak measured at 530 nm. The ratio of the fluorescent emission at 665 nm to that at 530 nm was used to measure endosomal acidification relative to that for untreated cells and is given as the average ± SD for 3 independent measurements. (B) EBOV GP-pseudotyped VSV pseudovirions were incubated with cathepsin B in the presence or absence of 50 μM each inhibitor. E64 served as a positive control that blocked cathepsin B activity. Proteins from treated virions were separated and immunoblotted for the GP and VSV matrix protein. Ratios of quantitation of full-length GP (uncleaved) to matrix protein were generated. Shown are the mean values ± SDs relative to the values for pseudovirions not treated with cathepsin B.