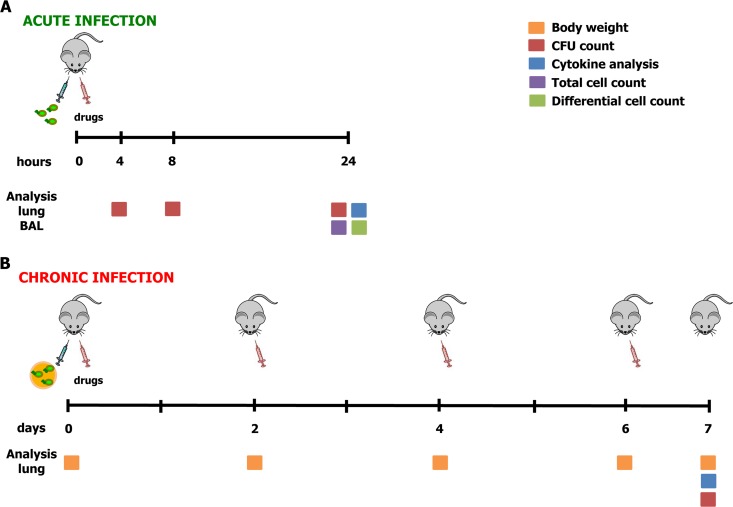
FIG 1.
Treatment schedule with antibiotics in murine models of acute and chronic P. aeruginosa RP73 infection and readouts. At day 0, mice were infected with P. aeruginosa planktonic cells to mimic acute infection (A) or with P. aeruginosa embedded in agar beads to achieve long-term chronic infection (B). The treatment schedule used with the antibiotics was administration of a single dose by the i.t. route for acute infection or administration every 2 days by endotracheal delivery for chronic infection. Readouts of the disease progression were body weight recorded before treatment or sacrifice (for chronic infection), CFU counts (performed at 4, 8, or 24 h for acute infection or after 7 days for chronic infection), total and differential cell counts (performed at 24 h for acute infection), and analysis of cytokines assayed at the time of sacrifice (performed at 24 h for acute infection or after 7 days for chronic infection).