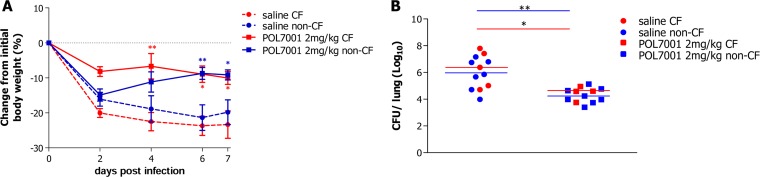
FIG 5.
Efficacy of POL7001 against P. aeruginosa RP73 in a CF murine model of chronic lung infection after aerosol administration. (A) C57BL/6 Cftrtm1UNCTgN(FABPCFTR)#Jaw mice and the corresponding congenic wt mice (11 to 18 weeks old) were challenged with 1 × 106 CFU of P. aeruginosa RP73 (embedded in agar beads) after i.t. inoculation. Aerosol treatment was performed by the use of a MicroSprayer Aerosolizer (Penn-Century) at 15 min postinfection and then every 2 days with either saline solution or POL7001 (2 mg/kg) for a total of four administrations. Before each administration, mice were weighed. Changes from initial body weight were calculated for each group of mice. Data represent mean values ± standard errors of the means (SEM). (B) At day 7, mice were sacrificed and lungs were excised, homogenized, and plated on TSA plates to determine bacterial load. The data are pooled from two independent experiments. Dots represent measurements from individual CF mice (red) (saline solution, n = 5; POL7001, n = 4) or congenic wt mice (blue) (saline solution, n = 7; POL7001, n = 8), and horizontal lines represent the median values. Statistical significance determined by two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni posttest is indicated in the body weight curves. Results of Mann-Whitney U test analysis are indicated in the CFU/lung data. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.