FIG 2 .
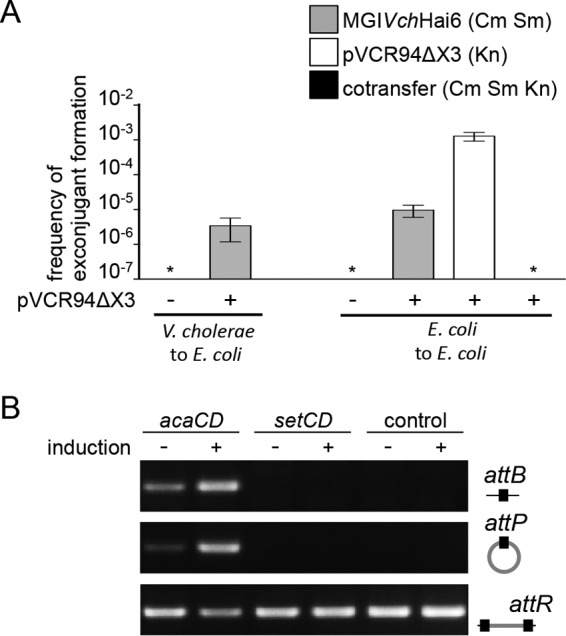
IncA/C-dependent excision and transfer of GIs. (A) MGIVchHai6 is mobilizable by ACPs. Inter- and intraspecific mobilization of MGIVchHai6 was assayed from V. cholerae to E. coli and from E. coli to E. coli, respectively. Interspecific transfer was done using V. cholerae HC-36A1 bearing pVCR94ΔX3 as the donor and E. coli CAG18439 as the recipient. Intraspecific transfer was performed using E. coli CAG18439 bearing pVCR94ΔX3 and MGIVchHai6 as the donor and E. coli MG1655 Rf as the recipient. Donor cells lacking pVCR94ΔX3 were used as a control. Exconjugants were selected for the acquisition of either MGIVchHai6, pVCR94ΔX3, or both. Transfer frequencies are expressed as the number of exconjugants per recipient CFU. Bars represent the mean and standard deviation values obtained from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate the frequency of exconjugant formation below the detection limit (<10−7). Cm, chloramphenicol; Sm, streptomycin; Kn, kanamycin. (B) AcaCD specifically induces MGIVchHai6 excision. Excision was detected by PCR on genomic DNA to amplify chromosomal site attB and the attP site resulting from the excision of MGIVchHai6 in E. coli. Integrated MGIVchHai6 was detected by amplification of the attR site. Assays were done employing E. coli MG1655 Rf strains bearing the single-copy integrated IPTG-inducible pacaDC3×FLAG vector (acaCD), the single-copy integrated IPTG-inducible psetDC3×FLAG vector (setCD), or devoid of plasmid (control), without (−) or with (+) induction using IPTG.
