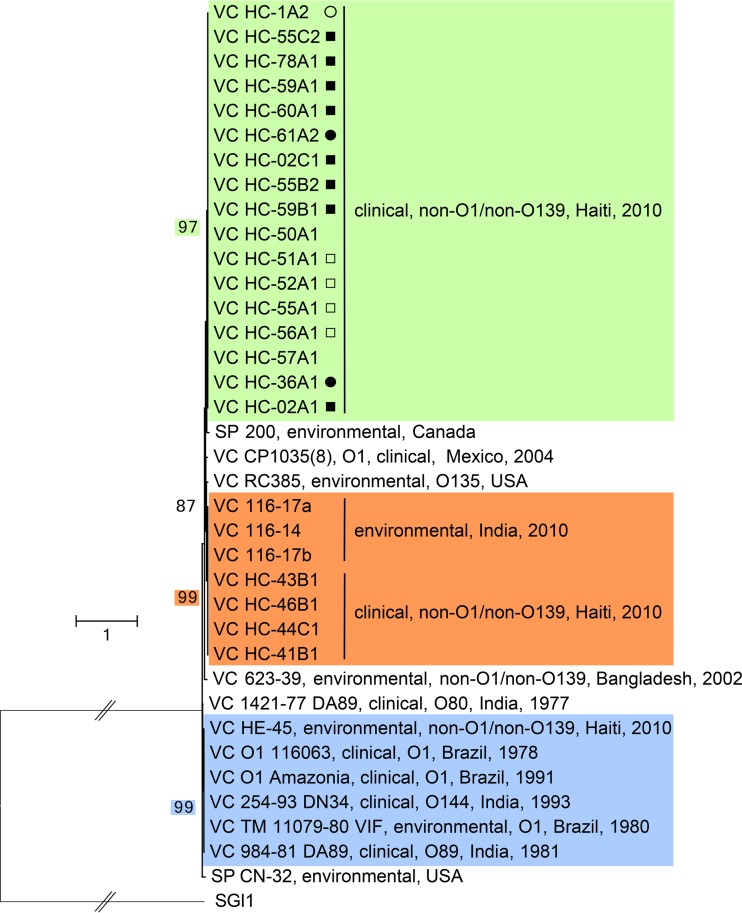
FIG 3 .
Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the attL-int locus of MGIVchHai6-related GIs by the maximum likelihood method. Based on the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model, the tree with the highest log likelihood (−5,618.1383) is shown (64). The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown only for bootstrap values above 80. Subgroups were defined as clades supported by at least 95 bootstraps and are color coded as follows: strains containing MGIVchHai6-like elements are in green, GIVchHai7-like elements are in orange, and GIVchBra1 to GIVchHai8-like elements are in blue. Because analyses were done on nonassembled draft genome sequences, symbols indicate the confidence that the strain contains a complete element (solid circles, complete MGIVchHai6; open circles, partial detection of In36A1; solid squares and open squares, complete or partial detection, respectively, of Tn6310 upstream of attR). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured by the number of substitutions per site. For clarity, the length of the branch linking the tree to the outgroup (SGI1) was artificially divided by 4. Vibrio cholerae and Shewanella putrefaciens are abbreviated VC and SP, respectively.