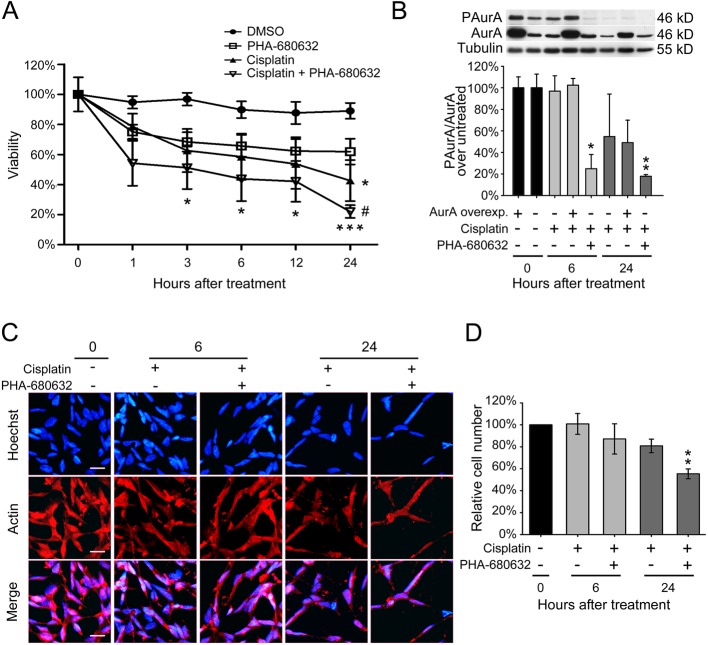
Fig. 3.
Combined treatment of cisplatin and PHA-680632 enhances cell mortality. (A) Residual viability in SK-N-BE cells treated for different hours with cisplatin and/or PHA-680632 (aurora kinase inhibitor). All treatment were performed after 4.5 DIV of differentiation and quantified through colorimetric MTT assay. DMSO treatment represents the control group. Data are given as mean±s.e.m. of percentage viability (N=3, each in triplicate). Statistical differences were assessed performing a two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni correction versus control. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, #P=0.012, one-way ANOVA versus aurora kinases inhibitor alone. (B) Densitometric quantification of phospho-aurora in SK-N-BE cells, double normalized on total aurora A protein of each culture, and related to untreated cultures with either normal levels (=100%) or with overexpressed aurora A kinase (=100%). Cells were treated for 6 or 24 h with cisplatin alone or in combination with PHA-680632 inhibitor. Upper panel: representative western blot with tubulin as loading control; lower panel: densitometric analysis from 3 independent experiments. Data are given as percentage mean±s.e.m. *P=0.01, **P=0.006; one-way ANOVA versus untreated control. (C) Immunofluorescence on SK-N-BE cells treated for 6 or 24 h with cisplatin alone or in combination with PHA-680632 inhibitor. Hoechst was used to highlight nuclei and actin was marked to emphasize cell bodies; the merge between the two channels is displayed. (N=3; scale bar: 20 µm). (D) Cell count from the immunofluorescence described in panel B. Values are given as mean±s.e.m. of percentage of cell number with respect basal condition (N=3). **P=0.003; one-way ANOVA versus untreated control.