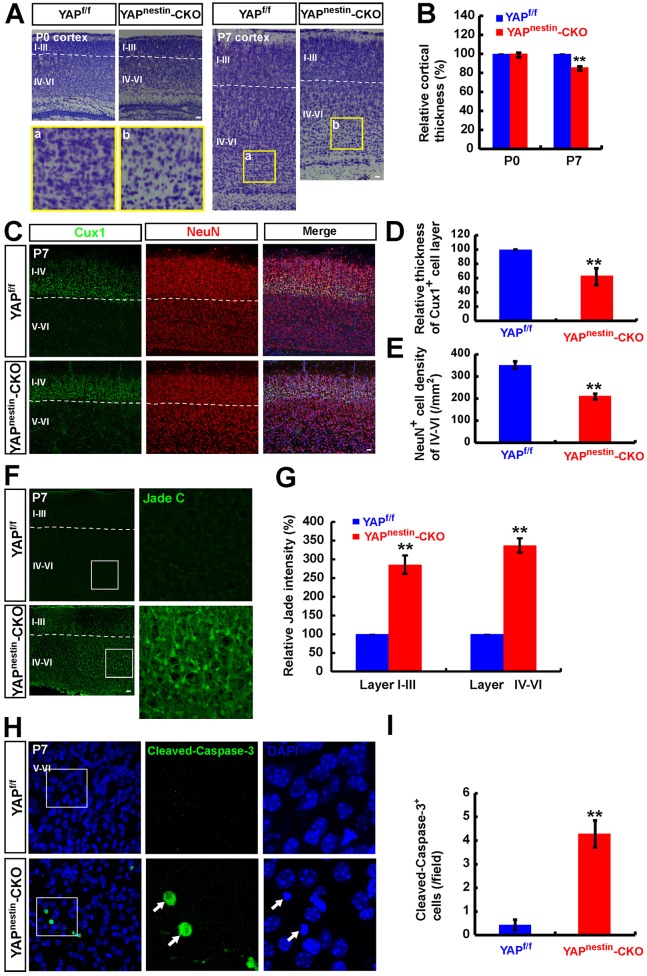
Fig. 6.
Increased neocortical neurodegeneration in Yapnestin-CKO brain. (A) Nissl stained images (sagittal sections) showing the brain phenotype of P0 and P7 Yapf/f and Yapnestin-CKO mice. Selected regions in P7 Yapf/f (a) and Yapnestin-CKO (b) mice are shown at higher magnification. (B) Quantitative analysis of neocortical thickness of P0 and P7 Yapf/f and Yapnestin-CKO mice (n=25 per group, normalized to WT group). (C) Double immunostaining analysis of CUX1 (green) and NeuN (red) in neocortex of P7 Yapf/f and Yapnestin-CKO mice (sagittal sections). (D,E) Quantitative analysis of the thickness of the CUX1+ cell layer (D, n=9 in Yapf/f mice, n=8 in Yapnestin-CKO mice) and the density of NeuN+ cells of layers IV-VI (E, n=8 per group) as shown in C. (F) Fluoro-Jade C (green) staining in the neocortex of P7 Yapf/f and Yapnestin-CKO mice. (G) Quantitative analysis of the relative intensity of Fluoro-Jade C (normalized to WT group, n=6 per group) shown in F. (H) Immunostaining analysis of cleaved caspase 3 (green) in layer IV-VI neocortex of P7 Yapf/f and Yapnestin-CKO mice. (I) Quantitative analysis of the number of cleaved caspase 3+ cells in each field (n=7 per group) as shown in H. Boxed regions are shown at higher magnification. Data are mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01, compared with control group, Student's t-test. Scale bars: 20 μm.