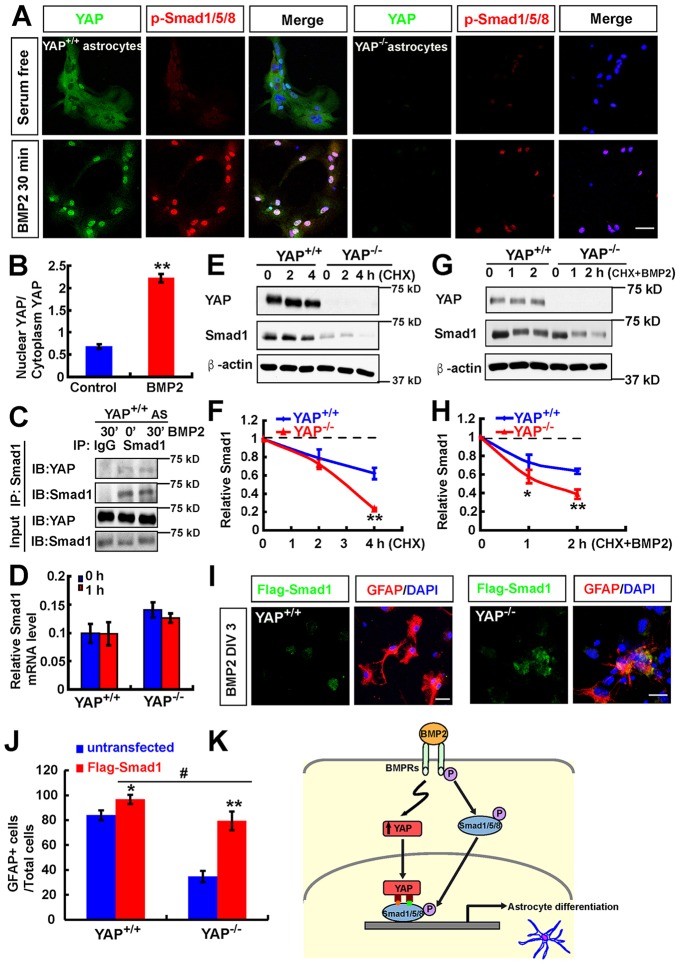
Fig. 8.
YAP stabilizes the BMP2-SMAD1 signaling. (A) Double immunostaining analysis of YAP (green) and pSMAD1/5/8 (red) in WT and YAP-deficient astrocytes before and after BMP2 treatment (100 ng/ml). (B) Quantitative analysis of the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic YAP in astrocytes before and after BMP2 treatment. (C) Western blot showing results of nuclear protein complex co-IP assays in WT astrocytes before and after BMP2 treatment (100 ng/ml). (D) RT-PCR analysis of the Smad1 mRNA level in astrocytes before and after BMP2 treatment (100 ng/ml). (E) Western blot showing YAP and SMAD1 levels in WT and YAP-deficient astrocytes before and after CHX (100 μM) treatment at the indicated time points. (F) Quantitative analysis of relative SMAD1 levels as shown in E (n=3 per group, normalized to 0 h). (G) Western blot showing YAP and SMAD1 levels in WT and YAP-deficient astrocytes before and after CHX (100 μM) plus BMP2 (100 ng/ml) treatment at the indicated time points. (H) Quantitative analysis of relative SMAD1 levels as shown in G (n=3 per group, normalized to 0 h). (I) Double immunostaining analysis of Flag (green) and GFAP (red) in WT and YAP-deficient NSCs transfected with Flag-SMAD1 3 days after BMP2 treatment (100 ng/ml). DIV, days in vitro. (J) Quantitative analysis of GFAP+ cells in WT and YAP-deficient NSCs transfected with Flag-SMAD1 or untransfected under BMP2 treatment (n=6 each group). (K) Model of YAP functions in neocortical astrocytic differentiation. BMP2 treatment promotes YAP nuclear translocation, and the nuclear/active YAP interacts with and stabilizes SMAD1 and is required for BMP2-induced pSMAD1/5/8 signaling and astrocytic differentiation. Data are mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with control group; #P<0.05, compared with WT control group after BMP2 treatment; Student's t-test. Scale bars: 20 μm.