Fig. 1.
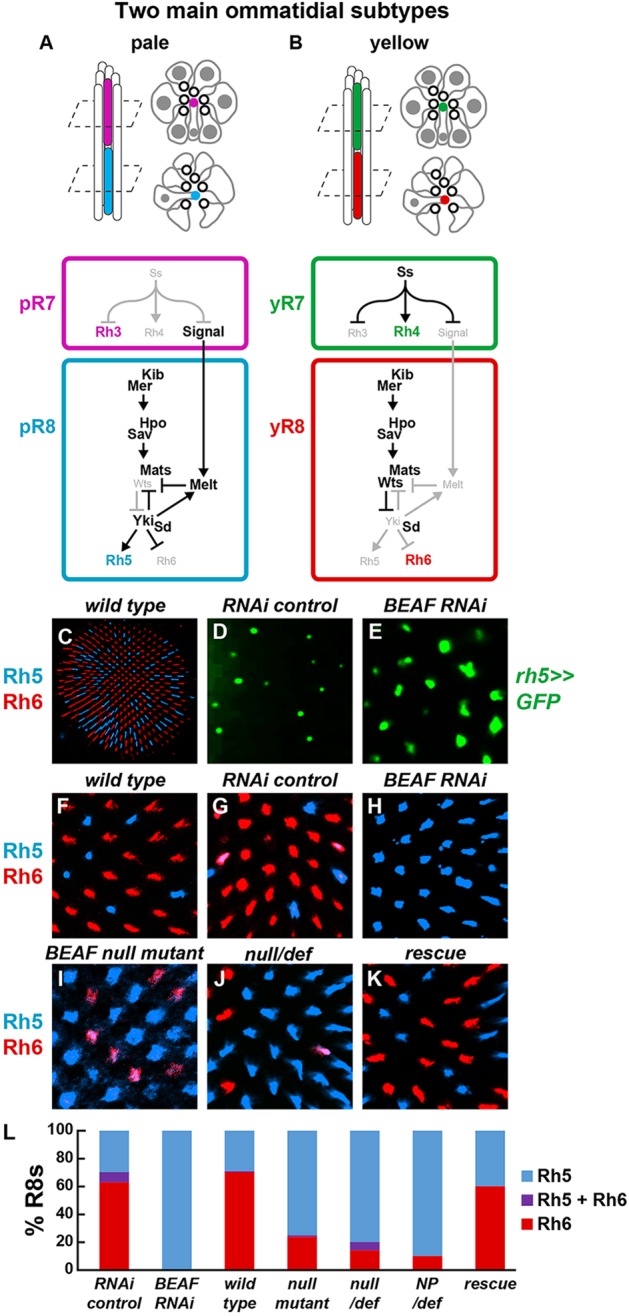
BEAF is required for yR8 subtype specification. (A,B) Schematic showing eight photoreceptors and a cross-section of their rhabdomeres, the membranous structures containing Rhodopsin (Rh) proteins, within an ommatidium. Gray indicates cell bodies and nuclei. White circles with black outlines indicate outer photoreceptor rhabdomeres. Colored rhabdomeres indicate R7 (top) and R8 (bottom). Below is the regulatory network controlling Rh expression in R7 (top) and R8 (bottom). (A) Pale ‘p’ ommatidial subtype. (B) Yellow ‘y’ ommatidial subtype. (C) Retina showing Rh5 and Rh6 expression in stochastic and mutually exclusive R8 subsets. R8 subtypes are visualized by Rh5 (pR8, blue) and Rh6 (yR8, red) antibodies in all panels unless otherwise noted. (D) rh5≫GFP was expressed in a subset of R8s in RNAi controls. Visualized by water immersion (see Materials and Methods). (E) rh5≫GFP was expressed in most R8s when BEAF was knocked down by RNAi. (F,G) Rh5 and Rh6 were expressed in subsets of R8s in wild-type (F) or RNAi Gal4 control (G) retinas. (H-J) Most R8s contained Rh5, and few contained Rh6, in retinas expressing BEAF RNAi (H) or homozygous mutant for BEAFAB-KO (I) or BEAFAB-K0 over a deficiency covering the BEAF locus (J). (K) A BEAF genomic fragment restored normal Rh5 and Rh6 expression in BEAF homozygous null mutants. (L) Quantification of phenotypes.
