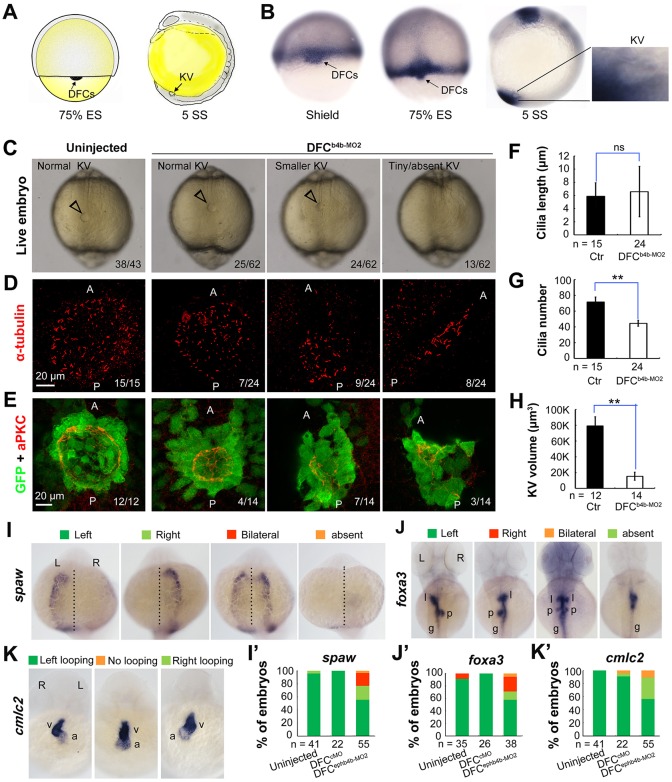
Fig. 2.
ephb4b is required for KV formation and LR asymmetrical development. (A) Illustration of DFCs at 75% ES (dorsal view) and KV at 5 SS (lateral view). (B) ephb4b expression pattern at the indicated stages. (C-H) Effects of DFC-specific ephb4b knockdown on KV size (C), cilia (D,F,G) and KV lumen (E,H) as analyzed at 10 SS. KV in live embryos (C) is indicated by open arrowheads and embryo ratios with different KV sizes are indicated. Cilia were visualized by acetylated tubulin immunofluorescence (D), and cilia number (F) and length (G) were analyzed. The apical surface of KV cells in Tg(sox17:GFP) embryos was labeled by co-immunostaining with anti-aPKC (red) and anti-GFP antibodies (green) (E), and the KV lumen size was measured on confocal images (H). A and P indicate the anterior and posterior sites of KV, respectively. In D and E, embryo ratios with the representative pattern are indicated. Error bars indicate s.e.m.; n, embryo number; ns, not statistically significant; **P<0.01. (I-K′) Effect of DFC-specific knockdown on spaw expression at 21 SS (I; dorsal views), foxa3 expression in liver (l), pancreas (p) and intestine (g) at 48 hpf (J; dorsal views), and cmlc2 expression in the ventricle (v) and the atrium (a) of the heart at 48 hpf (K; ventral views). The left and right sides are indicated by L and R, respectively. The proportions of embryos exhibiting each phenotype are shown in I′-K′.