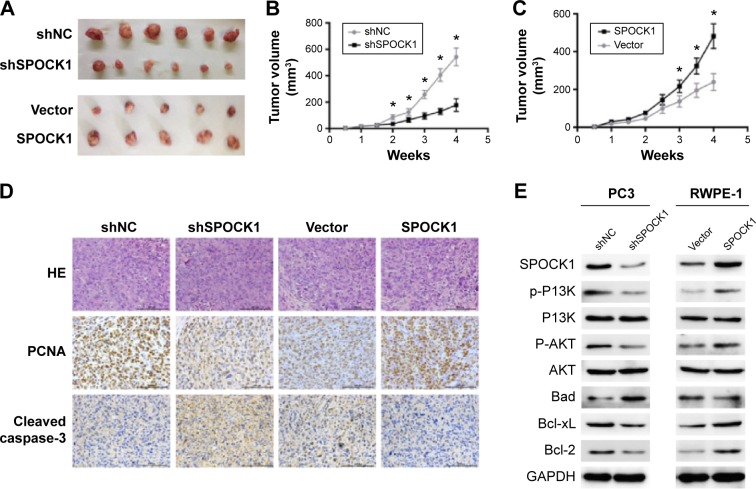
Figure 5.
SPOCK1 affected tumor growth in a mouse model.
Notes: (A) Tumor dissection showed that knockdown of SPOCK1 caused tumor size smaller, while overexpression of SPOCK1 enlarged tumor sizes. (B, C) periodic monitoring of tumor volume in PC3 cells and RWPE-1 cells in a consecutive of 4 weeks. (D) Histology and immunohistochemistry analysis of the sections from the mouse model. PCNA, a proliferation marker, and cleaved-caspase-3 were detected for indicating cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. (E) Immunoblot analysis of expression of SPOCK1 and a series of apoptosis-related proteins. It was observed that SPOCK1 positively regulated antiapoptotic factors Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL as well as phosphorylation kinases of Bad such as p-PI3K and p-AKT. The proapoptotic factor Bad was negatively regulated by SPOCK1 in both PC3 cells and RWPE-1 cells. *P<0.01.
Abbreviations: SPOCK1, SPARC/osteonectin, cwcv, and kazal-like domain proteoglycan 1; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; IHC, immunohistochemistry; p-PI3K, phosphorylated PI3K; p-AKT, phosphorylated AKT; HE, hematein eosin; shSPOCK1, shRNA against SPOCK1; shNC, negative control; GAPDH, reduced glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase.