Figure 1. Epigenetic post-translational modifications at histones associated with the Runx2/p57 promoter in developing hippocampus.
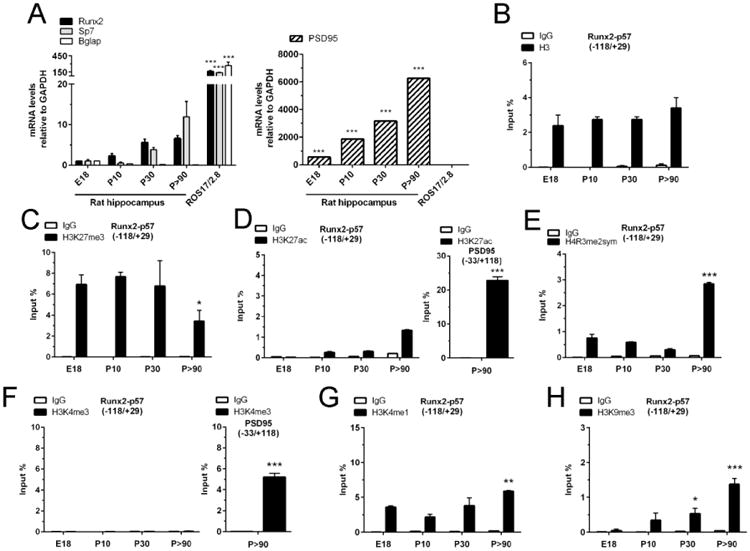
(A): Total RNA was extracted from E18, P10, P30 and P>90 rat hippocampus and mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR using specific primers. Results were normalized against GAPDH and expressed as fold change with respect to E18. Samples from rat osteosarcoma ROS17/2.8 cells were used as positive controls. PSD95 mRNA levels are represented with respect to Runx2 E18 expression (B-H): Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed on samples obtained from rat hippocampus at the indicated stages and incubated with antibodies against total histone H3 (B), H3K27me3 (C), H3K27ac (D), H4R3me2-symmetrical (E), H3K4me3 (F), H3K4me1 (G), and H3K9me3 (H). The precipitated DNA was quantified using specific primers against the indicated region of the Runx2/p57promoter. Primers for the PSD95 promoter region were used as positive controls. Results are shown as Input (%) ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Normal IgG was used as specificity control. *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, with respect to E18 (ANOVA). For the right panel of D and F, ***: P < 0.001, with respect to IgG (Student's t-test).
