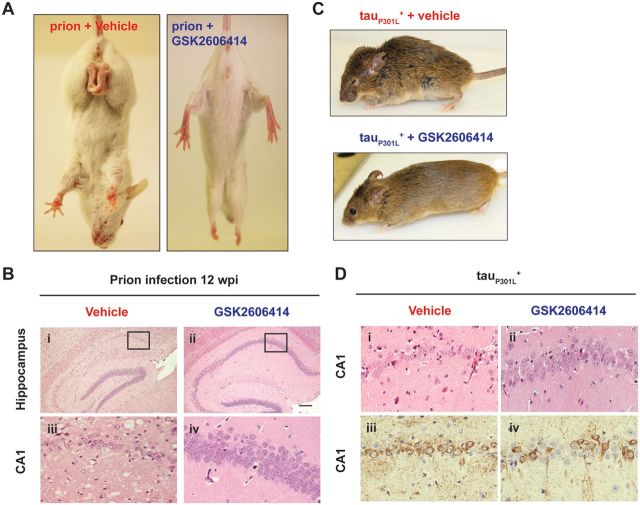
Figure 3.
PERK inhibition by GSK2606414 prevents clinical disease and neuronal loss in prion-diseased and frontotemporal dementia mice. (A) Prion-diseased mice were treated with vehicle or GSK2606414 from 7 weeks post-infection (wpi). At 12 weeks post-infection, GSK2606414-treated mice lacked the clinical signs of prion disease, with normal posture and movement of hind legs. (B) At 12 weeks post-infection, GSK2606414-treated prion-diseased mice showed marked neuroprotection in the hippocampus. (C) GSK2606414-treated frontotemporal dementia mice show normal grooming, posture and movement compared to vehicle-treated mice. (D) GSK2606414 treatment resulted in marked neuroprotection in the frontotemporal dementia mice, with the preservation of hippocampal neurons (i–ii). Immunostaining showed reduced levels of phosphorylated tau in the GSK2606414-treated mice (iii–iv).