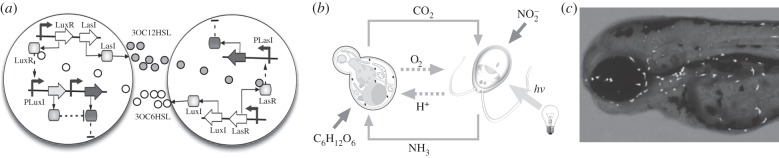
Figure 13.
Synthetic symbiosis. (a) A cooperative synthetic system involving designed auxotrophic interactions [150]. (b) Synthetic mutualism resulting from niche engineering. Here, two species interact through a metabolic circuit based on carbon and nitrogen exchange. S. cerevisiae (left) metabolizes glucose (C6H12O6) releasing carbon dioxide (CO2), which is then assimilated photosynthetically by C. reinhardtii (right) to release oxygen (O2). On the other hand, C. reinhardtii metabolizes nitrite (NO2) and releases ammonia (NH3) as a nitrogen source for S. cerevisiae [151]. In (c), we display a microscope image of a chimaera zebra fish embryo containing living photosynthetic cells [152,153].