Figure 7.
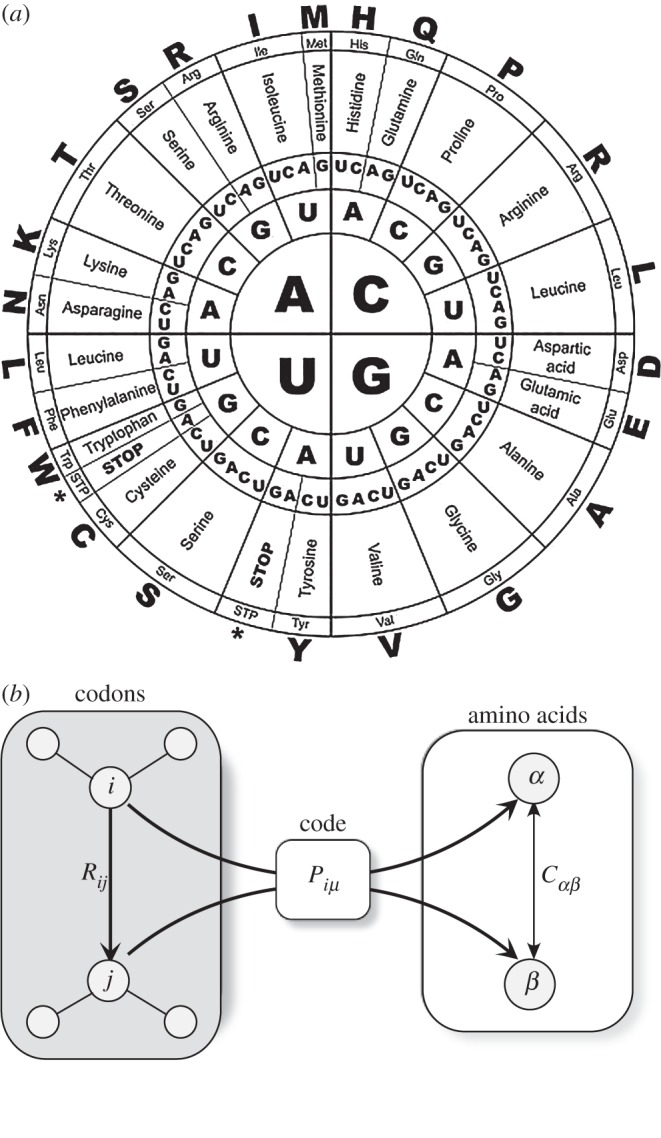
The universal character of the genetic code (a) and evidence for its optimality was obtained through an in silico analysis of millions of synthetic alternative codes, where the coding for amino acids (AAs) from the triplets defining codons has been randomly scrambled. (b) By treating the genetic code as a problem of information channels (b), we can find additional support for the optimality of the genetic code. Here, we indicate by Rij the probability of codon i being misread as codon j, whereas Piμ is the probability of codon i of encoding AAμ. The distance between AAs α and β is indicated as Cαβ.
