Figure 1.
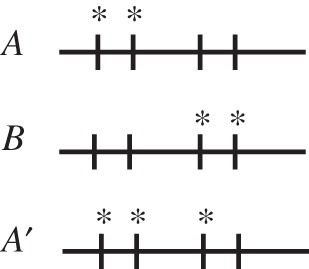
A hypothetical methylation pattern illustrates the loss of epigenetic information. Cell types A and B have different methylation patterns. Genetically encoded mechanisms transform A cell types to B and vice versa, during epigenesis. A’ is a new epimutant similar to A in the function that it performs in the multicellular body. The process that transforms A to B will also transform A’ to B. Since B can then not recreate A’, the epimutation is lost in differentiation.
