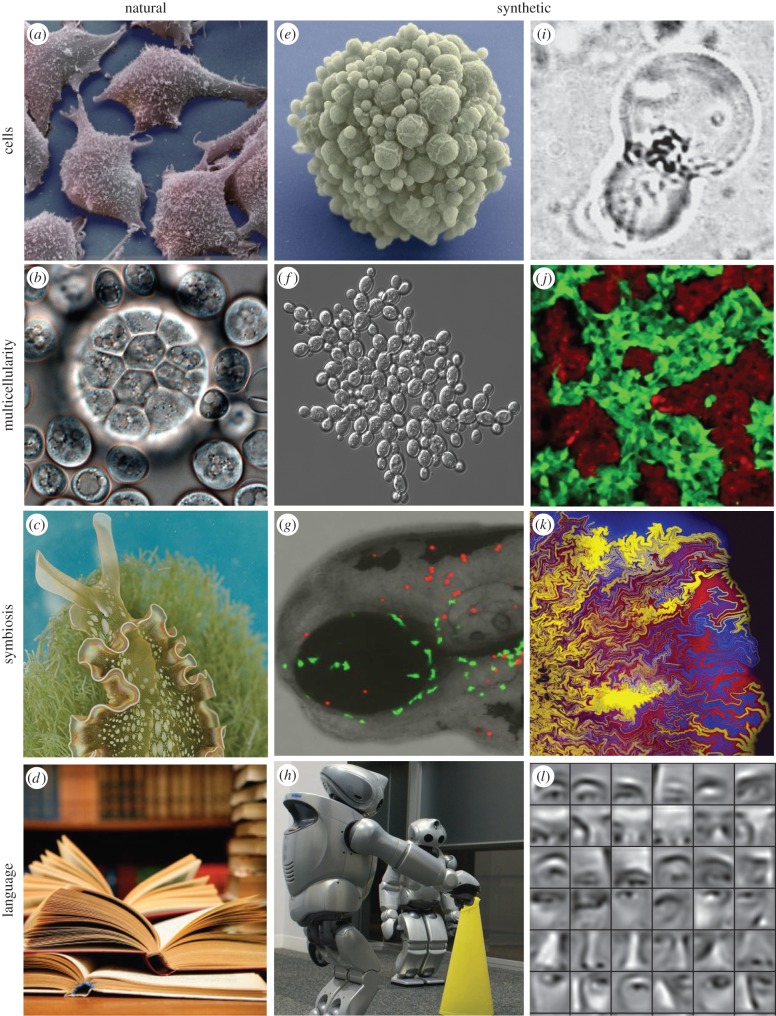
Figure 1.
Natural versus synthetic transitions. In the left column (a–d), four instances of observable types of evolutionary novelties are shown. From top to bottom, cells, multicellular systems, a symbiotic association between photosynthetic algae and a sea slug and language, as illustrated by written texts. The two columns on the right illustrate some examples of synthetic counterparts of these examples. These include synthetic cells using a genome reduction strategy (e) or a bottom-up protocell approach (i), evolved (f) and designed (j) multicellular systems, engineered cooperation (g–k) as well as evolved communicating robots and (l) artificial neural networks capable of pattern recognition and language processing.