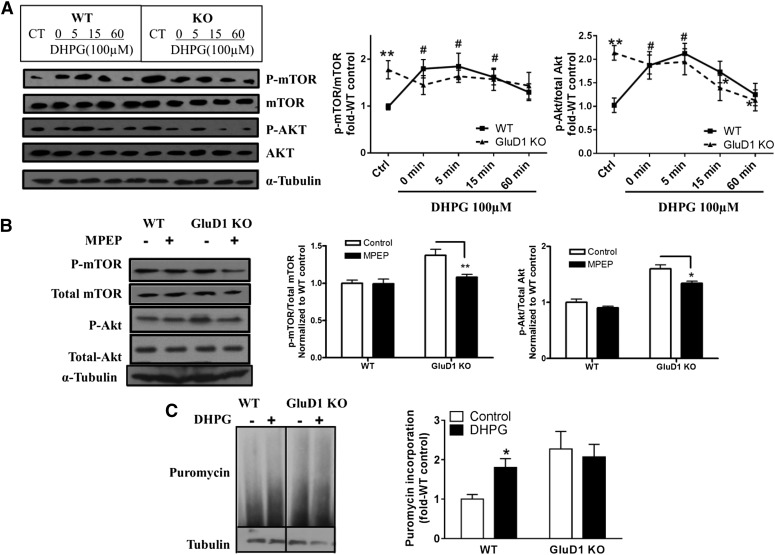
Fig. 3.
Elevated basal levels of phospho-Akt (p-Akt) and phospho-mTOR (p-mTOR) and lack of DHPG-induced p-Akt and p-mTOR increase in GluD1 KO. (A) Total protein from CA1 region of hippocampal horizontal sections was collected either with aCSF control treatment or after treatment with DHPG (100 µM, 5 minutes) for various times. Higher basal levels of p-mTOR (Ser2481) and p-Akt (Ser473) were observed in GluD1 KO (**P < 0.01, unpaired t test). An increase in p-mTOR and p-Akt levels was observed in the CA1 region in wild-type (WT) mice from 0 to 5 minutes after treatment with DHPG (#P < 0.05 compared with wild-type control, one-way ANOVA), but this increase was absent in GluD1 KO (N = 5–8 for each group). (B) Pretreatment with mGlu5-specific inhibitor MPEP (10 µM for 20 minutes) reduced the elevated p-mTOR and p-Akt levels in the GluD1 KO CA1 region (N = 4; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with GluD1 KO control, unpaired t test). (C) A significant genotype effect was observed in the puromycin incorporation assay to detect protein translation (N = 6; P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA). In addition, a significant increase in puromycin incorporation was observed with DHPG in wild-type slices (*P < 0.05, unpaired t test); however, this effect of DHPG was absent in GluD1 KO slices. CT, control.