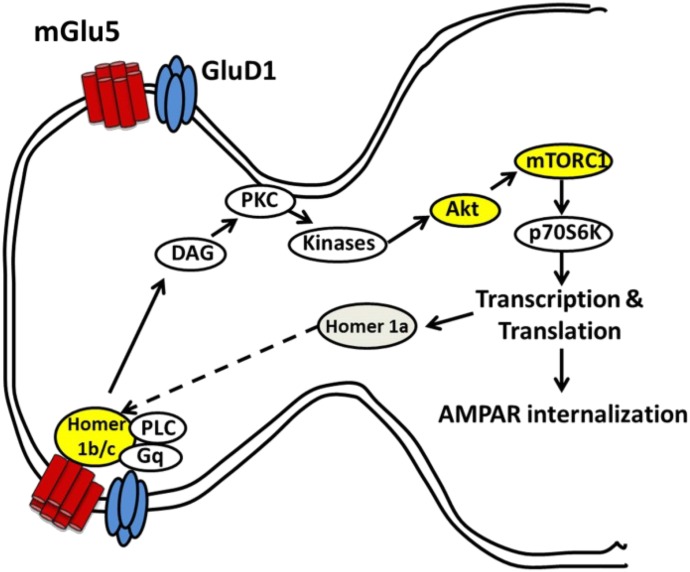
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of interaction between GluD1 and mGlu5 in the hippocampus. Our results demonstrate that GluD1 and mGlu5 colocalize at hippocampal synapses, and loss of GluD1 leads to a higher basal mGlu5-mediated Akt-mTOR signaling and impaired mGlu5 interaction with long-form Homer as well as a deficit in AMPA receptor (AMPAR) internalization. DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C.