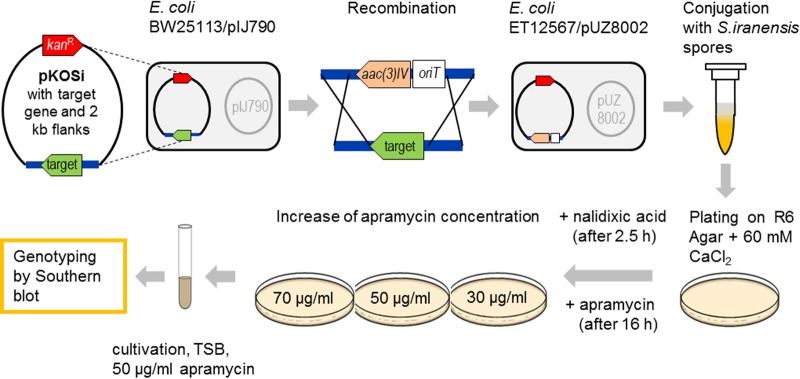
FIG 2.
Overview of the generation of S. iranensis gene deletion mutants via intergeneric conjugation. A PCR product consisting of a target gene and its 2-kb upstream and 2-kb downstream flanking regions was introduced into pKOSi (Fig. 1). The resulting pKOSi_SIRANxxxx plasmids were cloned via the shuttle host E. coli DH5α into E. coli BW25113/pIJ790, where gene rearrangement by homologous recombination with a disruption cassette occurred. The disruption cassette carried the apramycin resistance gene aac(3)IV and the origin of transfer gene oriT. Recombined plasmids were transferred into the nonmethylating E. coli strain ET12567/pUZ8002 for conjugation with S. iranensis HM 35. The conjugation mixture was plated on R6 agar containing 60 mM CaCl2. The growth of E. coli was inhibited by nalidixic acid. Obtained exconjugants were stepwise adapted to increased apramycin concentrations before genotyping by Southern blotting was performed to confirm successful genetic modification. TSB, tryptic soy broth.