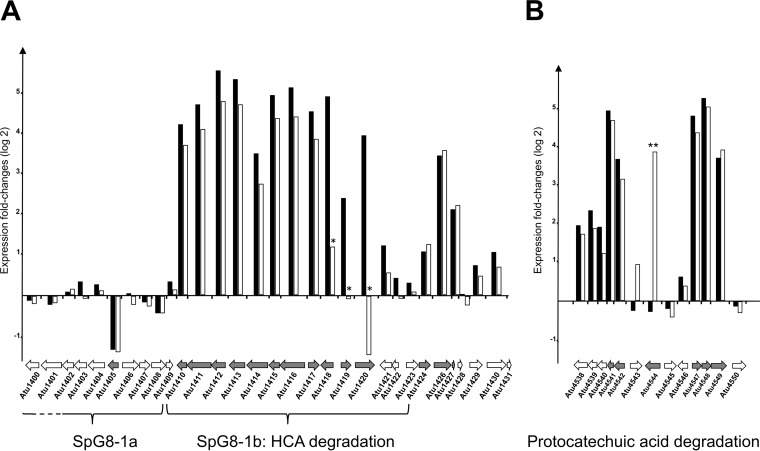
FIG 1.
Genomic regions differentially regulated in the presence of ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid. Each gene is represented by an arrow directed to the right for the gene transcribed from the plus strand and to the left for the gene transcribed from the minus strand. For each gene, histograms represent logarithmic fold changes in expression levels measured from cells cultivated with versus without ferulic acid (black bars) or with versus without p-coumaric acid (white bars). Gray arrows, genes with significant expression differences, according to ANOVA, at the 0.05 level, with the exception of atu1418, atu1419, and atu1420 (*), whose expression differences with p-coumaric acid were not significant. (A) The SpG8-1 region is subdivided into two regions, i.e., the SpG8-1a subregion, spanning atu1398 to atu1408, and the SpG8-1b subregion, spanning atu1409 to atu1423. Genes atu1415, atu1416, atu1417, and atu1421 are essential for the degradation of HCA, whereas atu1418 to atu1420 are essential only for the degradation of ferulic acid (3). (B) The region encompassing pca genes encodes the proteins involved in the second part of the HCA degradation pathway, i.e., the degradation of protocatechuic acid into acetyl-CoA and succinate. The gene atu4544 (pobA) is essential only for the degradation of p-coumaric acid, and its expression was significantly induced only with p-coumaric acid (**) (22).