FIG 8.
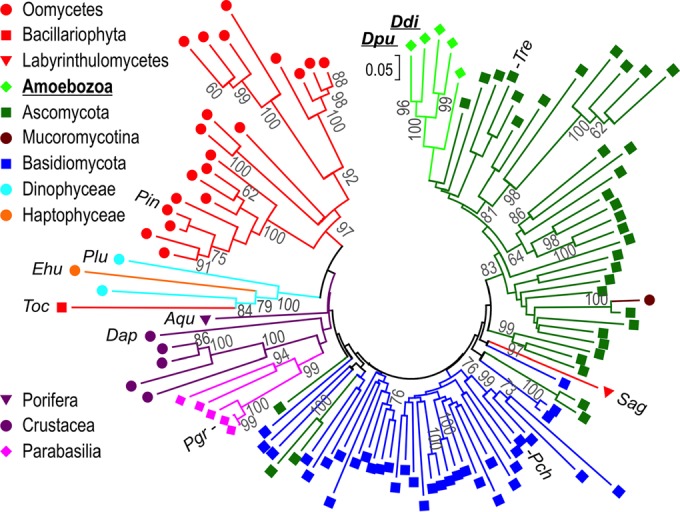
Phylogenetic tree of 113 GH7 CBH protein sequences. The evolutionary history was inferred using the minimum evolution method (58) with 700 bootstrap replicates in MEGA (v. 7) software (57) from a multiple-sequence alignment of the GH7 domain by MUSCLE, as described in Materials and Methods. Branch lengths are drawn to scale, with evolutionary distances, which were computed using the Dayhoff matrix-based method, being given in units of number of amino acid substitutions per site. Gray numbers are bootstrap values (in percent). A key to the colors and symbols is provided. Sequences listed in Figure 7 and Table 4 are indicated with the following abbreviations (UniProt accession numbers within parentheses): Ddi, Dictyostelium discoideum Cel7A (Q55FE6); Dpu, Dictyostelium purpureum Cel7A (F0ZJZ1); Tre, Trichoderma reesei Cel7A (P62694); Sag, Schizochytrium aggregatum (sequence from reference 76); Pch, Phanerochaete chrysosporium Cel7D (Q7LIJ0); Pgr, Pseudotrichonympha grassii (Q95YH1); Dap, Daphnia pulex Cel7A (E9G5J5); Aqu, Amphimedon queenslandica (I1FU52); Toc, Thalassiosira oceanica (K0T5R6); Ehu, Emiliania huxleyi (R1C7R5); Plu, Pyrocystis lunula (D8UXL6); Pin, Phytophthora infestans (D0N841). The complete tree with all sequence names is provided in Fig. S2 in the supplemental material.
