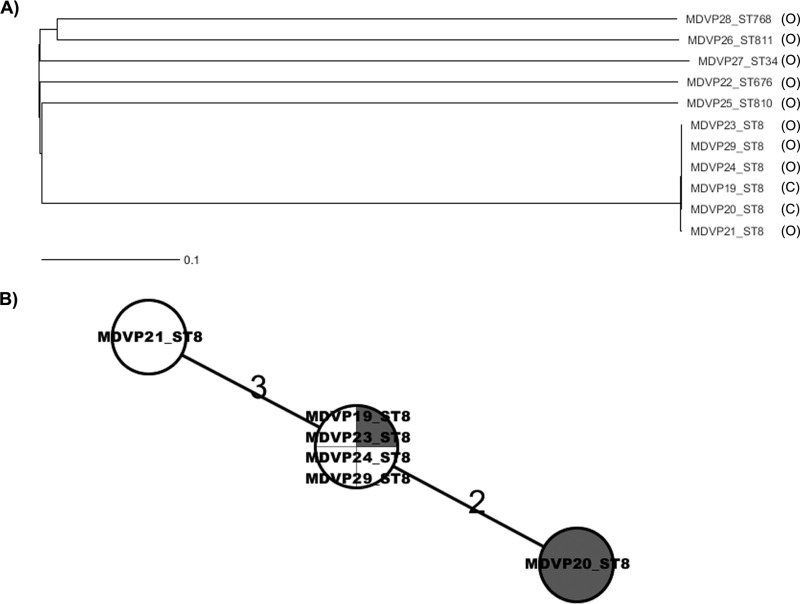
FIG 2.
Phylogeny of the V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated during the outbreak of 2010 in Maryland assessed by wgMLST analysis. Ridom SeqSphere+ identified 3,896 and 952 loci as core and accessory genes, respectively, for both chromosomes in V. parahaemolyticus. (A) NJ tree showing the high level of diversity of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from oysters and their relationship to the clinical samples (C, clinical; O, oysters) (3,955 loci were shared among the strains analyzed). (B) Minimum spanning tree showing the locus differences among ST8 strains from oysters (no shading) and from clinical samples (shaded). Of 4,349 loci shared by all ST8 strains, there were overall 5 loci differing among the strains, showing clonality of the strains. Also evident is that the ST8 oyster strains were indistinguishable from ST8 clinical strains. This result, combined with the epidemiological data, confirmed that the tested oysters were the source of the outbreak cases. The numbers above the connected lines are locus differences. The lines are not drawn to scale.