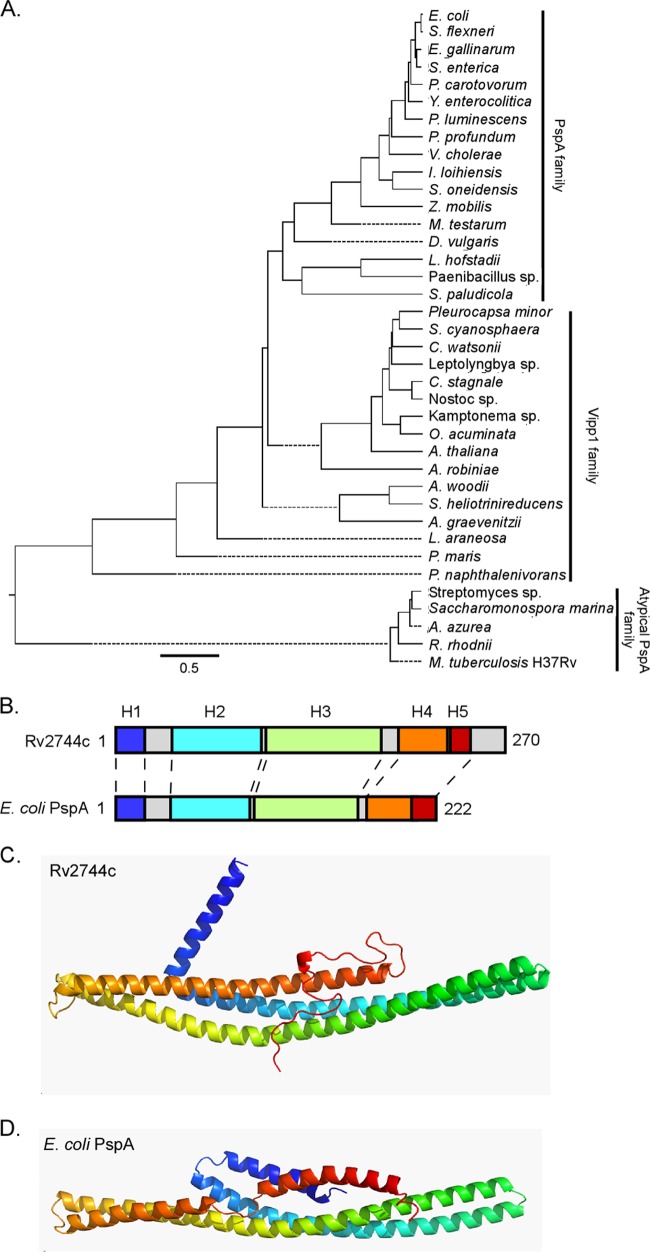
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic and modeling analysis of distantly related PspA family members. (A) Phylogenetic tree generated from representative protein BLAST search results with Rv2744c (M. tuberculosis), PspA (E. coli), and Vipp1 (A. thaliana) against bacterial and plant families, including Cyanobacteria, Actinobacteria, Spirochaetes, Fusobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Proteobacteria. Specific species analyzed included Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, Enterococcus gallinarum, Salmonella enterica, Pectobacterium carotovorum, Yersinia enterocolitica, Photorhabdus luminescens, Photobacterium profundum, Vibrio cholerae, Idiomarina loihiensis, Shewanella oneidensis, Zymomonas mobilis, Mastigocoleus testarum, Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Leptotrichia hofstadii, Paenibacillus sp., Sideroxydans paludicola, Pleurocapsa minor, Stanieria cyanosphaera, Crocosphaera watsonii, Cylindrospermum stagnale, Nostoc sp., Otoba acuminata, Arabidopsis thaliana, Actinospica robiniae, Acetobacterium woodii, Slakia heliotrinireducens, Actinomyces graevenitzii, Lentisphaera araneosa, Planctomyces maris, Polaromonas naphthalenivorans, Streptomyces lividans, Saccharomonospora marina, Amycolatopsis azurea, Rhodococcus rhodnii, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Representative proteins were selected for comparison if they either had an E value of <1 × 10−3 or were denoted as a phage shock protein A ortholog. Primary amino acid sequences were aligned via Clustal W alignment, and a phylogenetic tree was generated using MegAlign. Selected sequences were segregated into one of three major subgroups: PspA family, Vipp1 family, or atypical PspA family. (B) Despite their relatively low homology to each other, the PsiPred secondary structure prediction for Rv2744c and E. coli PspA revealed largely α-helical structures with similar organization (indicated as H1 to H5). Individual α-helical domains are denoted by color and are coded as described for panels C and D. The number of amino acids comprising each protein is also indicated. (C and D) Rv2744c (C) and E. coli PspA (D) were modeled via the Rosetta ab initio folding protocol and were colored N terminus (blue) to C terminus (red). Despite divergence in their amino acid sequences, the proteins appear to adopt similar folds composed of a central helix-helix domain.