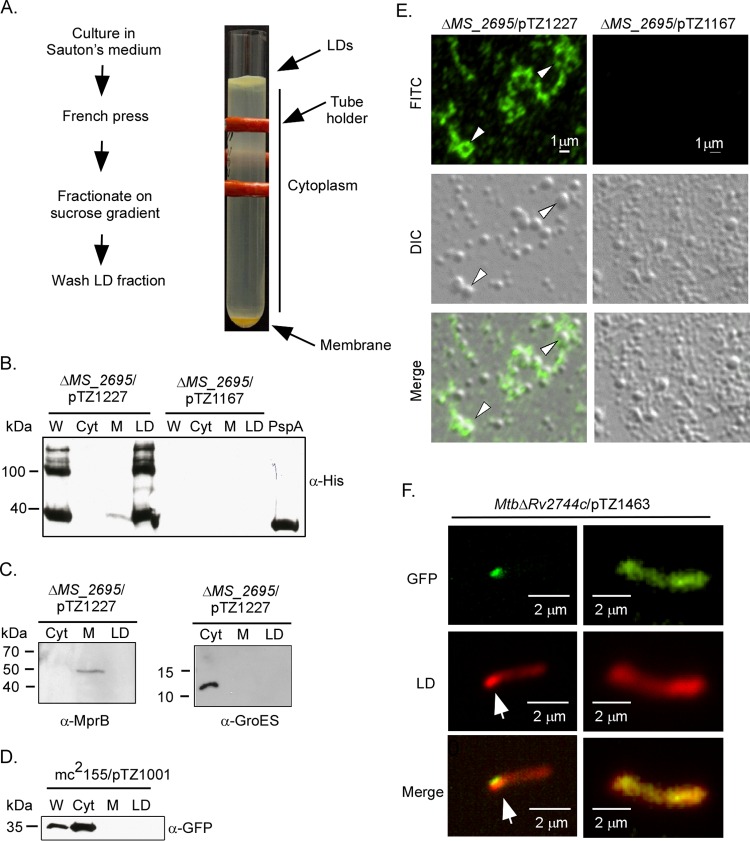
FIG 4.
Rv2744c localizes to lipid droplets in M. smegmatis. (A) Schematic of protocol used to isolate LDs from M. smegmatis strains and image of discontinuous sucrose gradient containing the buoyant lipid droplet layer floating on top, the region containing cytoplasmic proteins, and the pellet containing membrane-associated proteins. The red structure is a tube holder. (B) M. smegmatis ΔMS_2695 producing 3×FLAG-Rv2744c-6×His (pTZ1227) or M. smegmatis ΔMS_2695 carrying the empty vector control (pTZ1167) was fractionated via sucrose gradient centrifugation, and recovered aliquots were probed for 3×FLAG-Rv2744c-6×His by Western blotting. W, whole-cell lysate; Cyt, cytosol; M, membrane. The far-right lane contains recombinant Rv2744c-6×His purified from E. coli and included as a loading control. (C) M. smegmatis ΔMS_2695 producing 3×FLAG-Rv2744c-6×His was also probed with antibodies to sensor kinase MprB (membrane protein) and chaperone GroES (cytoplasmic protein) to confirm the integrity of our subcellular fractionation procedure. (D) M. smegmatis producing GFP (mc2155/pTZ1001) was cultured and processed as described above to isolate LDs. Fractions were then probed for GFP, showing proper cytosolic localization. (E) Immunofluorescence of LDs prepared from M. smegmatis ΔMS_2695 producing 3×Flag-Rv2744c-6×His (left) or M. smegmatis ΔMS_2695 carrying the vector-only control (right). Arrowheads indicate LDs in which Rv2744c completely surrounds the vesicle. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate channel; DIC, differential interference contrast used to observe LDs; merge, FITC and DIC channels combined. (F) Epifluorescence microscopy showing association of PspA-GFPmut3 fusion protein (FITC channel) with a region containing a cluster of Nile red-stained lipid droplets (tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate [TRITC] channel). Arrows indicate the region of lipid droplet accumulation within the bacterial cytoplasm.