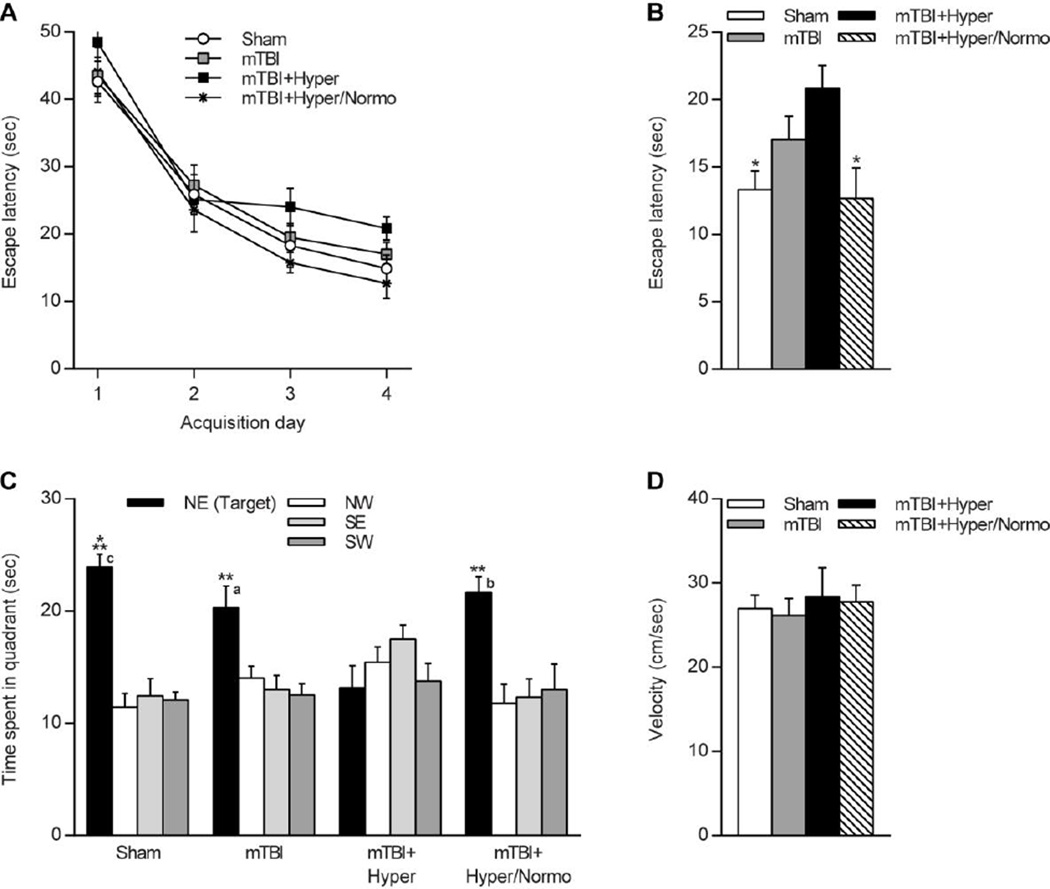
Fig. 2.
Effects of temperature manipulations on water maze performance after mTBI. (A) Escape latency to find the hidden platform across training days was not significantly different between sham, normothermic mTBI (mTBI), hyperthermic mTBI (mTBI+Hyper), or hyperthermic/normothermic mTBI (mTBI+Hyper/Normo) animals. (B) Analysis of escape latency on training day 4. Hyperthermic mTBI animals had significantly longer escape latencies as compared to sham animals or hyperthermic/normothermic mTBI animals. *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. (C) Retention of the water maze task by assessing time spent in the trained quadrant 24 h after the last acquisition day. Sham, normothermic mTBI, and hyperthermic/normothermic mTBI animals spent significantly more time in the target quadrant as compared to other quadrants. Hyperthermic mTBI animals had no significant increased time in the target quadrant. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 target quadrant vs other quadrants, one-way ANVOA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. Comparison of time spent in the target quadrant indicated that hyperthermic mTBI animals were significantly different than sham, normothermic mTBI, or hyperthermic/normothermic animals. ap<0.05, bp<0.01, cp<0.001 target quadrant time for hyperthermic mTBI vs other animal groups, one-way ANVOA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. (D) Swim speed was not significantly different between animal groups. n=12 sham animals, n=11 normothermic mTBI animals, n=11 hyperthermic mTBI animals, n=12 hyperthermic/normothermic mTBI animals.