FIG 4 .
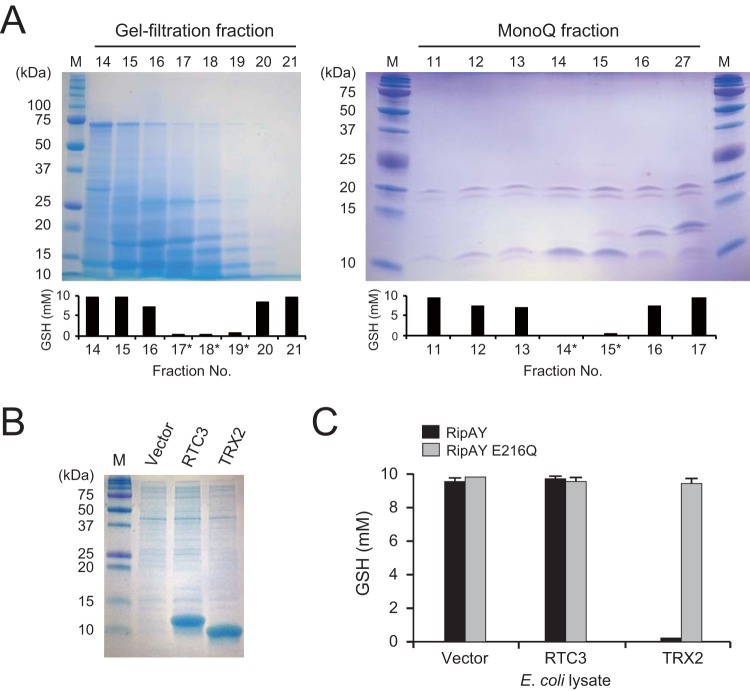
Purification and identification of yeast protein that activate RipAY. (A) Purification of RipAY activating protein from yeast cell extract by gel-filtration chromatography (left) and anion-exchange chromatography (right). After the dialysis of each 1-ml fraction, 1/10 vol of a sample was added to the reaction mixture containing 3 µg RipAY and 10 mM GSH substrate, and the mixture was incubated for 60 min at 30°C. Fractions surrounding the fraction showing RipAY activation were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (top panel). Fractions analyzed further are indicated by asterisks. The mean GSH level of three independent experiments is shown (bottom graph). (B) Lysates used for the RipAY activation assay. Lysates of E. coli strains expressing RTC3 and TRX2 were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (C) Activation of RipAY by recombinant yeast protein. Each E. coli lysate containing the recombinant yeast RTC3 or TRX2 protein was added to the reaction mixture and assayed for its capability to activate RipAY.