Figure 1.
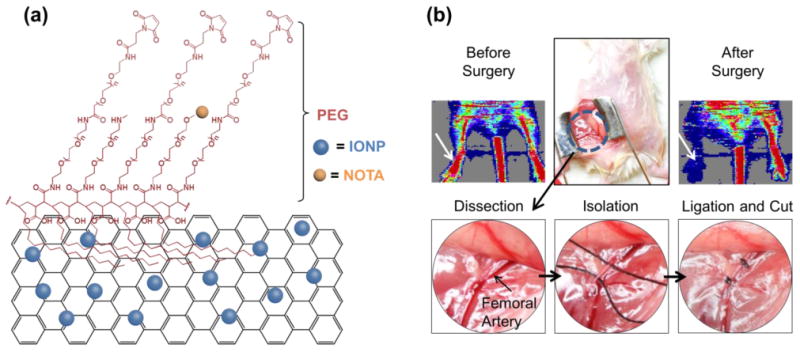
PEGylated reduced graphene oxide – iron oxide nanoparticles (RGO-IONP-PEG) for imaging of peripheral arterial disease in a mouse model of hindlimb ischemia. (a) Schematic drawing of RGO-IONP-PEG nanoparticle. On a sheet of reduced graphene oxide (RGO), iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) are conjugated (RGO-IONP). RGO-IONP was functionalized with NOTA and two layers of PEG. (b) The murine model of hindlimb ischemia is a representative model of human PAD. A mid-abdominal incision was made and the adjacent fat tissue and fascia were dissected to visualize the femoral artery for isolation, ligation, and cutting to produce the ischemic hindlimb. White arrow indicates the surgical hindlimb in the Doppler ultrasound imaging. Doppler ultrasound imaging revealed significantly decreased red signal in the ischemic hindlimb, indicating decreased blood flow and confirming the successful generation of the PAD model.
