Figure 1.
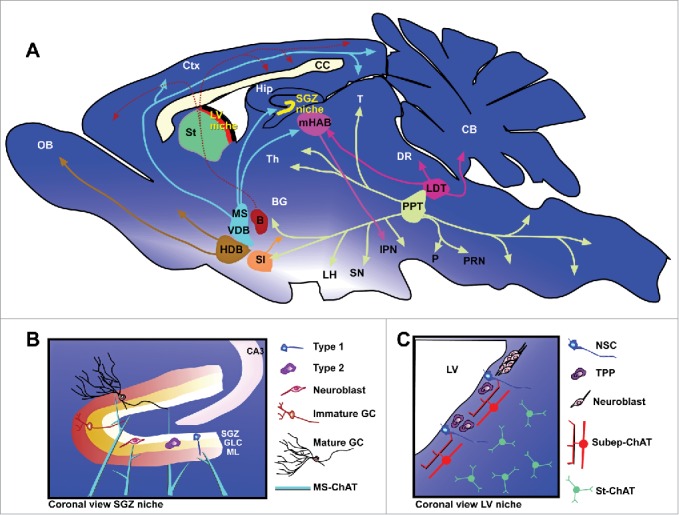
Cholinergic projections and neurogenic niches in the postnatal mouse brain. (A) Sagital section view showing major cholinergic nuclei and their known projections. Nuclei of the nucleus basalis group include: nucleus basalis of Meynert and magnocellularis (B); horizontal diagonal band of Broca (HDB); substantia innominate (SI). Nuclei of the medial septal group include: medial septal nucleus (MS) and vertical diagonal band (VDB). Nuclei of the pontine cholinergic group include: laterodorsal tegmental nuclei (LDT) and pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei (PPT). Other notable cholinergic neuron groups are found in: medial habenular nucleus (mHAB); striatum (St); and subependymal zone (SEZ). Major cholinergic neuron/nuclei projection targets include: basal ganglia (BG); cerebellum (CB); cortex (Ctx); dorsal raphae nucleus (DR); hippocampus (Hip); interpeduncular nucleus (IPN); lateral hypothalamus (LH); olfactory bulb (OB); pons (P); pontine reticular nucleus (PRN); substancia nigra (SN); thalamus (Th); and tectum (T). Neurogenic niches (LV and SGZ) are expanded in panels below. (B) Coronal section view of the SGZ neurogenic niche in the dentate gyrus (DG). Blue fibers indicate innervating projections from medial septal cholinergic neurons. Neurogenic cell types: astrocyte-like precursor (Type 1), transiently proliferating progenitor (Type 2), neuroblast, immature granule cell (GC), and mature GC. GLC = granule cell layer; ML = molecular layer of the DG. (C) Coronal view of the LV neurogenic niche, showing subep-ChAT neurons as well as neighboring striatal cholinergic neurons (St-ChAT). Neurogenic cell types include: (NSC) neural stem cell, Mash1+ transiently proliferating progenitor (TPP), and neuroblasts.
